Data hierarchy: Structure and organisation of data involving fields, records, and files.
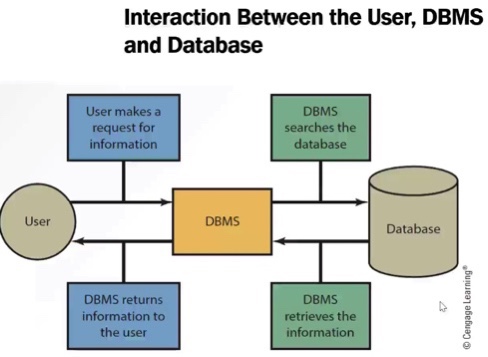
Database management system (DBMS): A DBMS is a collection of programs that enables to store, retrieve, update and delete information from a database. It enables management of data. It provides the users with the processes of defining, constructing and manipulating data for various applications. It is a logically coherent collection of data with some inherent meaning, representing some aspects of the realworld and it is designed, built and populated with data for a specific purpose.
It provides ways to organize, store, retrieve, and interact with the data. DBMS consists of:
A modeling language, which is leveraged to define database schema, or structure. Common database models include hierarchical, relational, network and object-based. These models differ in how they connect related information. The most commonly leveraged, particularly in web applications, is the relational database model.
A database engine that manages the structure and optimizes the storage, whether that is records, fields, objects or files for a balance between quick retrieval and efficient usage of storage space.
A transaction mechanism that validates data against allowed types before storing them in the DBMS and ensures that multiple users cannot update the same data simultaneously, thus potentially avoiding the corruption the data.
A database query language like SQL that enables to write programs that extract data from the database, presents it to the enduser, and save and store updates. Collection of related data is stored in a central location or in multiple locations.
Software for creating, storing, maintaining, and accessing database files. Making using databases more efficient.
Types of Data in the Database
- Internal : Collected from within the organisation. It is stored in the organisation’s internal databases.
- External: Comes from a variety of resources. It is stored in data warehouse.
Methods for accessing files:
Records can be accessed in any order irrespective of the physical locations in storage media.
Fast and very effective when a small number of records need to be processed daily or weekly.
Records are stored on magnetic tapes.
Logical Database design
Physical view: Involves how data is stored on retrieved from storage media. Example: Hard disks, magnetic tapes, or CDs.
Logical view:
Involves how information appears to users and how it can be organised and retrieved.
Includes more than one logical view of data, depending on the user.
Logical Database design
Determine how data is created, represented, organised and maintained. It contains data structure, operations and integrity rules.
Hierarchical model: Relationship between records form a treelike structure.
Relational model: It has primary key and foreign key. The primary key uniquely identifies every record in a relational database. The foreign key is a field in a relational table that matches the primary column of another table. It is used for cross reference tables. Normalised data helps improve database efficiency by eliminating redundant data. It ensures only related data is stored in a table. It goes from first normal (1NF) to fifth normal form (5VF). This model retrieves data from tables using operations that pick and combine data from one or more tables. The operations used are: select, project, join, intersection, union and difference.
Recent trends in Database design and use
Data-driven website: It allows interface to a database. It retrieves data and allows users to enter data. It improves access to information. It gives users more current information from variety of data sources.
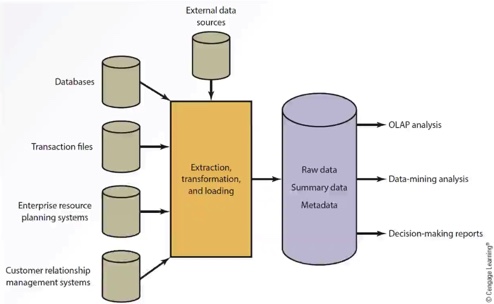
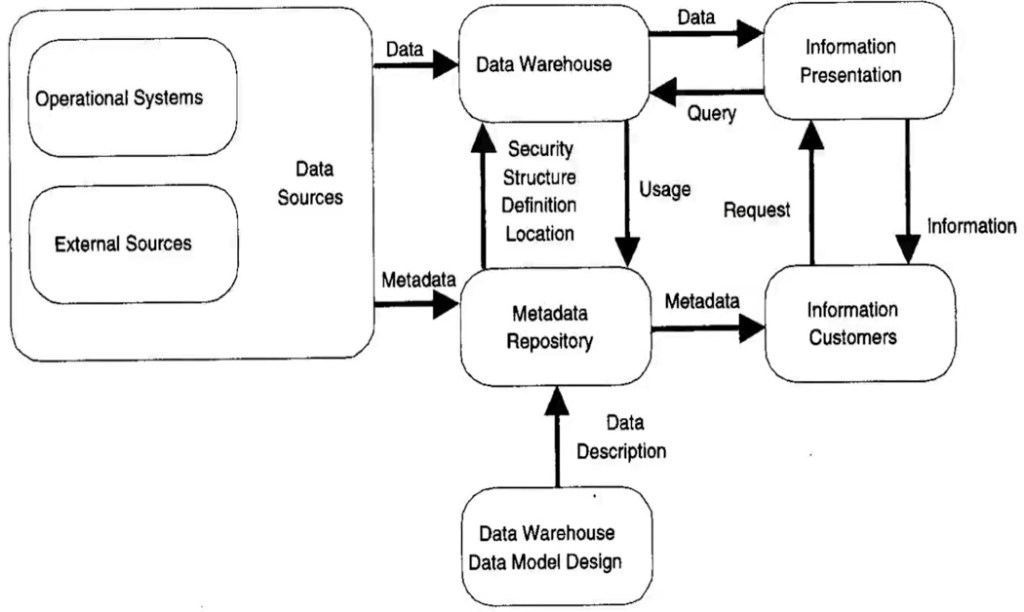
Characteristics of data in a Data Warehouse: It is subject oriented. It comes from a variety of sources. It is categorised based on time. It captures aggregated data. It is used for analytical purposes.
Multidimensional Data Modeling
Designed to facilitate analysis and not transactions. It is common in data warehousing. It is the intuitive concept of many dimensions or perspectives on business measures or facts. View sales from customer, product and time perspective. It is a conceptual model.