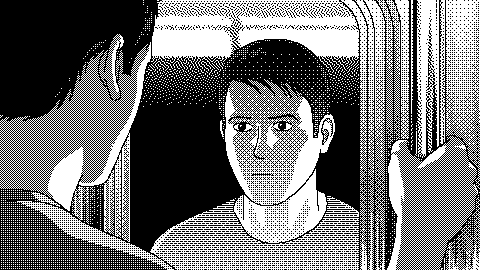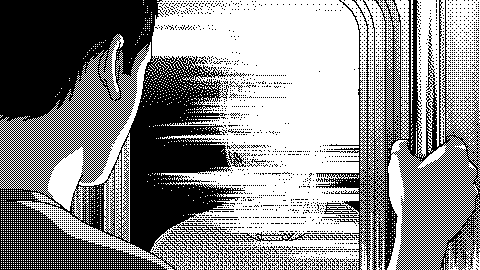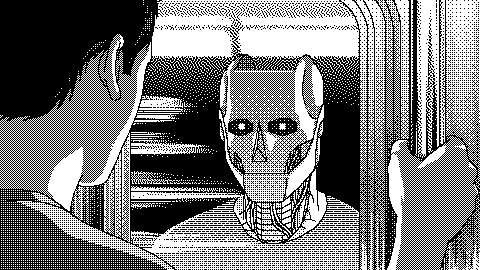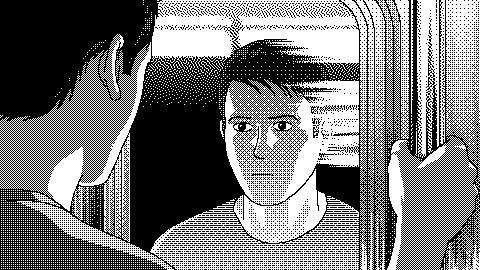
Self driving cars. When cars drive all cars can drive. AI is about unleashing power amazing things in the universe. AI is growing exponentially and it is changing our world differently. Intelligent thermostats, autonomous robots to self driving cars are an example of Artificial Intelligence.
Overview of Artificial Intelligence
Super AI: It is very intelligent.
General AI: Chatbot.
Navigation is computational hard problem. They have space complexibility. The best choice may not be the optimal path. We are using direct distance heuristics to decide which step to explore next. A* search is the most effective and popular algorithm out there. An intelligent agent like self driving cars can react to other cars and anticipate to them. We need to keep care of orientation while taking actions but the goal needs to be final locations.
Heuristic is some additional piece of information- a rule, function or constraint – that informs an otherwise brute force algorithm to act in a more optimal manner.
Goal: Use search strategy similar to the route finding problem to design an AI that can play Tic Tac Toe. What should be the nodes and edged?
A:
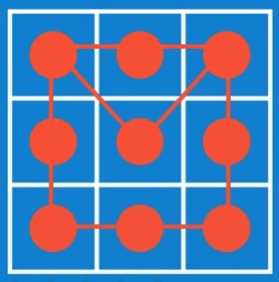
B: Use the current position of the computer player as a node, expressed as a row/column tuple where row, column are {0,1,2}. Two such nodes can be connected if their row and column differ by at most 1.
Edges :
(0,1)-(0,2),
(1,0)-(1,1)
Mini max algorithm: You trying to maximise your chances of winning on your turn, and you opponent it is trying to minimise your chances of winning on their turn.
Probability theory gives formal mechanics to helps us make sense in the real world and make sensible decisions when we’re uncertain. Probabilistic modelling is applying statistics to data Analytics. Naive Bayes, Logistic is an example.
Prior probability: 1/total outcomes

Bayes theorem: (1*0.33)/0.5 = 0.66
Humans are intelligent at doing a lot of different things. Equating intelligence with human behaviour will rule out all artificial systems. artificial general intelligence should be defined within a task.
Environment: Understanding the task or problem domain is key to designing systems. The intelligent system or software is called as the agent. The software is the agent. The hardware system like sensors, motor, hardware is external to the environment. The result the agent is trying to attain is called agent. The agent senses the environment through sensors and this is called as perception. By process by which an agent decides which action to take is based on perceived input is called as cognition. Cognition is used for reason and decision making. Some agents directly perceive their actions with what they see. These are known as behaviour based agents. Game play agents or path planners are examples of non-trivial processing by agents. These can be further classified as knowledge agents, learning agents, planning agents etc.
Types of AI problems
Properties of the environment and state of the environment.
Fully observable environment state is tic-tac-toe. Partially observable environment state is Battle field. Environment can be deterministic or stochastic. It can be discrete where there are finite state of environment or continuous where the number of states is infinite. Some properties needs to be stored as real numbers. An environment could be benign where the agent is the only one taking action which intentionally affects score or adversarial where there are one or agents to beat its score. This is mostly found in competitive games. Environment states could be playing poker, recognising handwritten text, driving on the road and playing chess.
Playing poker would be partially observable as one cannot see the opponents name. Or it could be stochastic as the player doesn’t know which cards are to be dealt in with. It’s discrete as there are finite number of hands. It would be adversarial and there are two opponents trying to win.
Recognising handwriting text is stochastic as there’s lot of randomness there. There are lot of possibilities, although there are finite representations the underlying observation is continuous. It’s not adversarial.
Driving on the road is partially observable as the cars cannot be seen completely on the road. Self driving cars cannot predict without information in real world so they are continuous. It’s not adversarial.
Playing chess is fully observable, it’s discrete. It’s also non-stochastic and adversarial as there’s competition.
Intelligence takes action to maximise its utility for a given desired goal. This is known as rational behaviour. It requires agents to behave optimally. It’s extremely hard to find the optimal solution. We need to consider the constraints the object faces such as limited computational resources such as memory, processing speed, rules imposed at hand given at deadlines etc. Given the constraints we cannot expect the agent to behave optimally. We can have level of performance we want the agent to perform. For example: We would want computer chess to win at-least 60% of the time against human player. This is called as bounded optimality which is for feasible method for quantitative intelligence.
- Constraint Propagation
When trying to solve a problem, you’ll find that there are some local constraints to each square. These constraints help you narrow the possibilities for the answer, which can be very helpful. We will learn to extract the maximum information out of these constraints in order to get closer to our solution. Additionally, you’ll see how we can repeatedly apply simple constraints to iteratively narrow the search space of possible solutions. Constraint propagation can be used to solve a variety of problems such as calendar scheduling, and cryptographic puzzles. - Search
In the process of problem solving, we may get to the point where two or more possibilities are available. What do we do? What if we branch out and consider both of them? Maybe one of them will lead us to a position in which three or more possibilities are available. Then, we can branch out again. At the end, we can create a whole tree of possibilities and find ways to traverse the tree until we find our solution. This is an example of how search can be used.
How artificial intelligence is changing the future of Digital marketing
Artificial Intelligence is the ability of a computer program or a machine to think and learn. It is also field of study which tries to make computer smart. It works and react like humans it works and react like humans.
In a normal computer program, we give input to the system and it gives as output. But using AI and machine learning we give system is an output and as them to build the input. Artificial intelligence has the role in programmatic advertising. It means sending write message to the right person at the right time. An automated, technology driven method of buying and selling online ad space. In the traditional world, we used to buy an ad space might directly talking to the publisher like TOI, NDTV etc. They can guarantee only the impressions and no commitment of gone with conversions.
Modern digital marketer is want white Audi of opportunities and to measure every going to spend on the media. This thought has introduced programmatic advertising to marketers. Programmatic advertising in AI advertisers to buy at space is an audience across lakhs of 50 sites. this work how do I know where my heart is running and who is seeing it? This is where the role of AI comes. It’s called DSP (demand side platform), he is a system that allows buyers of digital advertising inventory to manage multiple at exchange and he text changer accounts through one interface.
It uses machine learning to target audience across sites and apps. Predicting in planning. Campaign optimisation. Better targeting capabilities. AI driven creative. Data driven and insights.
Best practises for driving performance:
- Partnering with the right platform
- Sending the right signals to the platform
- Said camp and goals and KPIs
- Utilising first, second and third party data to drive the efficiency
- Audience strategy – prospecting, behavioural, re marketing
- Building strategy – optimise for CPM, CPC, CPA
Why is it important for marketers to understand the role of AI in DM
It is very simple: These computer program uses various signals sources to understand the right audience, creative mix, placements, beats, budgets, demographics, and many other things to reach the right user that you may want for your business.
One of the main an important source of information lights with us that is brand. Feel assistance with the right input like cool, but, budget, conversion actions like install even, sign-up and 46 and try to drive the maximum results out of the campaign types.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are going to disrupt traditional marketing
50% of work activities could potentially be automated by today’s technologies, and 80% of them is enabled by machine learning
What it helps in?
Customer acquisition
Intelligence discounting
Personalisation
Media optimisation.
Role of AI and universal app campaigns
What is universal app campaigns?
It’s an ad campaign type that allows brands to advertise on some of Google’s largest ad networks including search, display, YouTube and the Google play store using the Google ads platform with very minimal campaign set up process.
Setting up in US the campaign takes not more than 10 minutes and you can get very limited options for optimising these campaigns.
Why you should not worry about the limited options available on UAC to optimise the campaign type?
USC works completely on machine learning.
It integrates AI and ML into every face of app promotion.
Targeting is completely automated to help drive to scale, as Willis efficiency.
Creative optimise using machine learning basis the cold you set it up.
Automatic placement selection using machine learning.
And it uses thousand of signals like online behaviour, time of the day, devices, age, gender, location and many more to target an user.
This is my marketers need to understand how AI and machine learning functions. It is still vital that you understand human input that goes into successfully utilising UAC.
Even though the campaigns type uses the machine learning to drive results, it needs to have the right inputs (export import) to drive the result you want.
What are the inputs?
Pick the right goal for your campaign (install or in app you want)
Set the right KPI Target (CPI or CPM)
Set the right budget.
Have right set of creatives (compelling creative, right sizes and formats)
Conversion tracking
Why is it important?
Choosing the wrong type of UAC goals can make or break a campaign
Making too many changes to budget and KPIs leads to fluctuations.
Not using creative assets report will lead to poor performance.
Never set up this type of campaign without using conversion tracking.
Artificial Intelligence Expert systems are software programmed with expert knowledge to either recommend or make decisions. They are used in: interpretation, prediction, diagnosis, delete, planning, monitoring, instructions and debugging.
Deep mind -Artificial General Intelligence
2010 was found started Deep-mind by three founders. The valuation was more than 600 $ million. It was acquired by Google in 2014. IBM Watson supercomputer was based on AGI. Starcraft II- Alpha star and Atari 57 games – Agent 57.
AI is two type: specialised and generalised. AGI is a sub part of AI. specialised does specific task like Siri, recommendation system, Instagram filter, etc. but they don’t have any IQ. AGI is bringing intellectual skills to the machine.
MinMax algorithm is used for TicTacToe. It is used for GameTheory like checkers, chess which has less power of complexity. The algorithm will play the game till it gets the maximised score. Th agent will play till it gets the minimised score. AI is trying to visualise the minimum and the maximum score. It will play every possible game and come with minimum and maximum % of wining and loss.
Supervised: Train the model based on the input. We are supervising it. It takes a lot of time to train the model.
Unsupervised: Games suitable as there’s no training data. The machine self learns itself by scratch
Reinforcement learning:
Q-value: quality of an action at a state. Estimate of how good it is to take an action. Q(State, Action) = Q value
A high Q value for an action means the end reward will be high. It helps determine how good it to take a particular action.
Q learning is a value based reinforcement learning algorithm which uses Q values.
Responsible AI
Responsible AI should be included in policies, programs and services in the government programs.
What’s AGI?
By combining several weak AI systems—we can develop strong AI. This strong AI or AGI agent will be capable of human-level performance at many broadly defined tasks. AI achieves human-level performance, some researchers predict this strong AI will surpass human intelligence and reach so-called superintelligence. Estimates for attaining such superintelligence range from as little as 15 years to as many as 100 years from now.
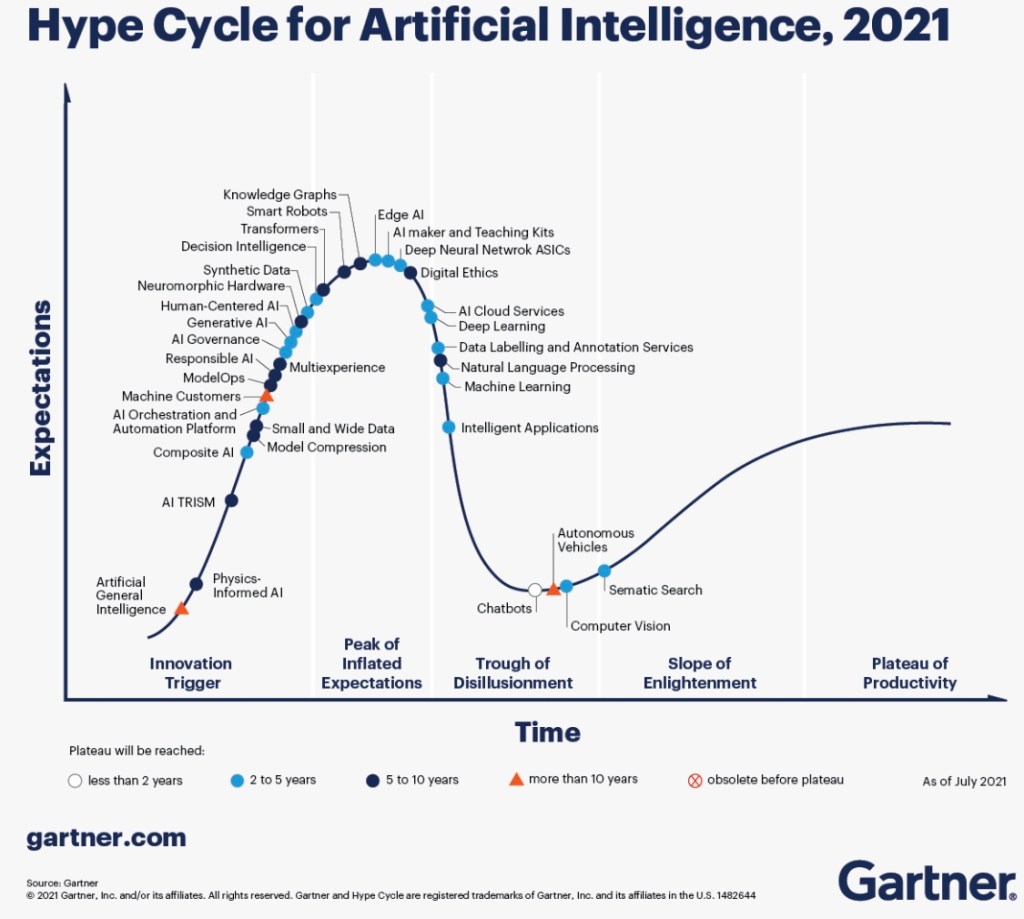
Development is moving faster than users, and AI is being used for coding. However, white coding and models are introducing vulnerabilities. 80-90% of web applications and DevOps backend scripts are affected. Web levels are also vulnerable, and hardcoding keys is not fully functional. JavaScript injection is another issue. Despite these challenges, models are getting better at security.
Risks and considerations
Several factors need to be considered before implementing an application to ensure it meets the required standards and ethics and safety.
Trust and accuracy:
– Accuracy of data inputs and output results.
– Overreliance on given information without due diligence on sources.
– Explainability and traceability of outputs.
– Identifying the supervising applications required to appropriately monitor all applications.
– Ensuring that all output information is rigorously validated.
Privacy, surveillance, and security
– Data collection with unclear use. Will sensitive data be made public during the next training round?
– Determining the ethical surveillance applications of GPT.
– Verifying that the organisation maintains clear and personal data privacy.
– Maintaining comprehensive cybersecurity control over its environment.
Fairness and bias
– Bias towards certain subgroups due to public training data.
– Bias in model can drive unfair outcomes in some business applications.
– Managing toxicity in responses requires ongoing management.
– Identifying the controls and measures used to check for bias.
– Ensuring that ethical considerations align with the organization’s standards.
Legal and regulatory
– Potential copyrights and IP infringement.
– Liability of use.
– GPT compliance.
– Verifying that the organisation is meeting regulatory and compliance standards.
– Determining the level of human oversight needed to verify compliance.
– How the organisation will continue to evolve as technology improves.
Al journey pillars that will unlock value creation opportunities.
Strategy: Every enterprise will need to rethink its strategy and operations—from new business models and products/services to redefined business processes—by putting human and machine together at the centre.
Al journey pillars: Rethinking the enterprise requires organisations to assess where they are on their journey and where to allocate resources and investments to accelerate their journey.
Confidence in Al: governance, legal, and risk: Organisations must navigate a dynamic legal and regulatory landscape as Al continues to evolve globally, while establishing guardrails and curated sources of truth to remain trusted.
Accelerating adoption and integration: Accelerating the adoption and integration of Al across the enterprise to support existing technologies, capabilities, products, and services will prove highly valuable.
Equipping and upskilling your workforce: By leveraging Al, organisations can unlock the full potential of their workforce, including completely reinventing learning and development programs.
Functional transformations: Organisations will face transformations across their functions—supply chain, distribution, and customer experience—which will require every process and system to be rethink.
AI framework
The AI framework outlined includes several key components to manage and govern AI models effectively:
1. Definition of AI: Clearly defines AI to classify models within the scope of the framework.
2. Three Lines of Defence Operating Model: Implements a RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) model with a governance committee structure to oversee AI activities.
3. AI Governance Framework: Establishes a framework for governing AI operations.
4. AI Risk Appetite: Defines the acceptable level of risk associated with AI models.
5. AI Enterprise-Wide Policy: Develops a comprehensive policy for AI use across the organisation.
6. Ethics and Privacy: Includes principles and policies, along with assessment questionnaires, to ensure ethical use and privacy protection.
7. Model Risk Tiering Framework: Classifies models based on risk and maintains an inventory of AI models.
8. Data Risk Policies and Infrastructure: Manages data risk through policies and designs data infrastructure like Data Lakes and Cloud solutions.
9. Data Strategy: Outlines a strategic approach to data management.
10. Vendor Tools and AI Training: Manages vendor tools and provides AI training at all organisational levels, including a third-party risk framework.
11. Technology Strategy: Focuses on the technology infrastructure needed for model development and deployment.
12. Use Case Scoring and Prioritisation: Establishes criteria for scoring and prioritising AI use cases.
13. Model Validation Guidelines and Framework: Provides guidelines and a framework for validating AI models.
14. Model Development Guidelines: Includes guidelines for developing AI models, with a Fairness Assessment Framework and an Explainability Framework.
15. Ongoing Monitoring Framework: Implements a framework for continuous monitoring of AI models.
Validating data
Validating data involves ensuring its accuracy, uniqueness, completeness, and representativeness. This includes selecting a suitable sampling strategy for data splitting and key statistics comparison. Additionally, feature exclusion is crucial to identify and address sparse features and those with zero variance.
Data infrastructure must be scalable to accommodate large data inflows, ensuring accessibility to real-time data, as many algorithms require it. Minimising latency is essential to reduce the time delay between requests and responses.
For big data, the data management pipeline should be adaptable to vast datasets. Unstructured or semi-structured data requires governance and cybersecurity controls.
Warehousing should incorporate variable transformation and model-independent feature engineering, such as transforming date-related variables, to enhance data quality. Imputation and remediation techniques should be assessed for their impact on missing data and outliers.
Data should be free from bias, ensuring it is not skewed and free from the specified categories of bias. Warehousing should aim to maximise the number of items processed per time unit, and storage systems must be able to handle concurrent demand.
Establishing SLAs with external vendors and verifying the reliability of external data sources is crucial for external data integration. Data security and protection measures should be enhanced to safeguard data access, ownership, collection, storage, and transmission.
Cloud data lake storage should be secure and reliable. Agile remediation techniques are necessary for dynamic AI models, allowing for quick and effective response to changing requirements.
Component principles for data warehousing:
– Data storage strategy and infrastructure: The data storage strategy and infrastructure should support AI applications and balance storage performance, ease of data management and handling, and cost.
– Scalability: Given that AI models require a vast amount of data, the data infrastructure should be scalable and accommodate a constant inflow of newly collected data.
– Parallel access: Optimisation of AI models often requires splitting activities into multiple parallel tasks, which leads to simultaneous access to the same file from multiple processes. Storage systems must be able to handle concurrent demand without impacting performance.
– Accessibility: Data must be continuously accessible as AI models are often used in a real-time environment, and efficient real-time data access is crucial.
– Throughput: Data warehousing should maximise throughput (number of items processed per time unit, e.g., terabytes per hour), especially as AI models use a vast amount of data.
– Latency: Data warehousing should minimise latency (time delay from system request to response completion), especially as AI data is reread several times (e.g., for model training).
Generalised Artificial Intelligence has substantially changed the traditional approach to data strategy. Data strategy has evolved into a knowledge strategy. Data quality has transformed into knowledge curation, data integration into context engineering, and planning into understanding the knowledge required to run a business, making data accessible, and identifying and sourcing data for specific use cases. Data serving involves using use case identification and data sourcing to process data, ensuring accessibility, and designing a data storage architecture. Model implementation, development, monitoring, and documentation are also crucial aspects of data strategy.