Hazard: An incident that has the potential to kill people and cause economic loss.
Mitigation: Make the structure safe in the area. It has much more effect than disaster relief. Do a safety audit to know which building is safe. Shift the people from the area. The area before the earthquake itself. Know about dams in the earthquake as it will lead to floods. Mass education on how to save their life in case the earthquake occurs.
- Vaccination
- Health insurance
- Life insurance
2. Response
3. Relief
They occur without a warning. Everything in the ground is liable to get damaged.
The biggest recorded was Valdivia Earthquake with a magnitude of 9.5 on the Richter scale
The place where the earthquake occurs is the epicentre.
Movement of waves in-ground, releasing of energy.
What can be done as part of disaster management?
Is there is a township of 20000 people:
- Fire brigade needs to be close.
- Necessary equipment to tackle fire at 20th floor.

Environmental laws, rules and Audit
Planet Earth:
Lithosphere has an average depth of 5-7 kms.
Crust: Where we people are living. It is the thinnest layer. Apple’s skin peel.
Mantle(semi-liquid): rocks and magma
Rock, largest layer. Magma is molten.
Outmost layer: core.
Earth is rotating in tilted axis. Every layer is moving simultaneously. Temperature is proportional to pressure. At the centre the pressure is maximum with high temperature. The speed of rotation of core is 2/3 times faster than crust, magnetic induction
We all are surrounded by magnetic induction and gravity.
Molton liquid is in under tremendous pressure and high temperature. Molton is surrounded by 82% mantle. A gap is generated in the mantle due to the high temperature and pressure. It comes out to crust. When tectonic plates move away, the lava come out as volcanic eruption.
Why is it a disaster?
Through the action of gravity it will move. Anything that comes in contact with lava will burn.
There are 100s and 1000s of under volcanic eruptions (tsunami).
350 tsunami on daily basis.
- Volcanic eruptions on land
- Volcanic eruptions on water: Tsumani.
It is 4.56 billion years old.
Temperature is very cool, life generates, life multiplies, Temperature increases to high level so mass extinction happens. Again the temperature comes down. So new life comes. This process repeats. Every era has shown the same trend of rise in temperature and extinction.
Human species came 0.2 million years. We are the youngest species of this planet. Human was absent there was no economic development, no industries, no depletion of fossil fuels. Climate change is not a man-made process.
Global warming is a natural process scientifically. The rate at which the global warming is taking place is far more than the natural global warming is.
Natural increase is 0.6 degrees above normal in 20,000 years.
22 years: 0.6 degrees increased
- degree in less than 2 centuries
1800-1970: 0.6 degree
1970-1992: 0.6 degree, species declined 256 per year. Rate of recovery 1 specie per year.
1800-1900: Humans followed pattern. Chemical energy for mechanical energy.
1900- Chemical to electrical energy to mechanical energy
Heavy consumption of fossil fuel leads to establishment of thermal and nuclear plants. Green has gases were in the atmosphere.
1970: 0.6 degree rise above normal
1970-1992: another 0.6 degree C rise
1990: most populated decade
1992: 0.6 degree C rise. 3000 species extinctions.
2020: 1.9 degree above normal, more than 6000 species extinction.
Even if we have sufficient technological advancement.
Even the slight increase my cause phenomenal alterations like health, forest, coastal area, water resources, biodiversity,
Because of biodiversity we are living in this planet. Food is coming from biodiversity.
Bio-diversity: Bio means life. Diversity means variety. Variations in life form.
Indonesia has 450 varieties of food to eat. Drugs and medicines come from biodiversity. We are deriving vaccine, enzyme, hormone, vitamins and making
Our body can’t produce particular sets of vitamins. We have to depend on other species.
UND report more than 50% medicines come from nature. Our body needs vitamin D from sun also vitamin B1 we have to grab from other sources.
Biodiversity is highly affected by climate change. Natural selection is a highly accepted theory,
Natural rate of extension of species is 1 specie per year simultaneously 1 specie is evolving each year. The last individual is gone forever that is considered extinction.
256 species per year, rate of evolution is 1 specie per year (recovery).
6200 species is going extinct each year. It’s a great loss for nature in terms of ecosystem productivity.
Species never go extinct in isolation. Species goes extinct due to huge disturbance in the surroundings.
Dodo bird was a flightless bird, it lived in Mauritius and Madagascar.
island. 1000 hectares of rainfall. Population of dodo started declining. As dodo got extinct, after 10 years, the 1000 of hectares of tropical rain forest cover was gone without any human interference or without any disease in forest or any disaster. Studies found that Dodo used to consume tropical plant seeds. The seeds used to pass through the dodo’s digestive system it wasn’t able to germinate. The outer layer was very hard and it used to dissolve in the Dodo’s digestive system. Whatever came out was the soft seed. No seed germination lead to no plant population, the species dependent on planet wasn’t able to make it. Within a stretch of 2 decades the entire forest was gone.
Services provided by the environment is externalised by the economy. Species recycle the carbon dioxide emitted by us. Today we chop off the trees. This is done by the literate class.
Until and until we internalise the issues of environment in economy we won’t be able to frame solutions for the environment around us.
Most vulnerable committee is reptiles they lay eggs in summers.
Summer comes in late winters. Biological activity of reptiles gets activated in late winters. They spawn in late winters. Summers are more harsh.
Reptiles are cold blooded they can’t tolerate heat of summers. There is 70% decline in reptile population over 5 decades.
Flowering and fruiting is dependent on temperature. Plants don’t know when to bloom. Global warming has caused a lot of seasonal disturbances. After 1970s agricultural revolution, it was predicted that 20% of the food will be gone. We aren’t even half way for food security yet. We had agricultural change, industrial change but that also lead to planet change simultaneously.
60% population only eats once a day. We have disturbed climate change.
Majority of the human population is living on coastal line. Most of 65% of human race globally lives in coastal areas.
Major are present in coastal area like Mumbai, Dubai, Hong-Kong, Sydney. Hurricane, cyclone,
If anything happens to coastal area our economy will be shattered.
March 2011, disaster of Japan, shut down of stock market for a week. 3 states economy was completely done.
Arma hurricane in Atlantic Ocean. September 2017, Larsen sea iceberg disintegrated in Antarctica (South Pole). Due to this disintegration, India is on the verge of losing its luxury island. According to metrological Department, sea level is rising. The island is submerging. Who is responsible for it. It’s our activities in the tropics that such activities intensify.
70% of the planet earth has been recognised with water stress. Water stress has a direct connection with climate change. Satellite data has proven that air pollutant come up to the atmosphere through winds they are transported towards the ocean, once they are transported over the ocean they form a layer over the ocean, once they form layer the sunlight is not able to heat the ocean as it gets scattered due to layer of pollutants.
Surface of ocean is not heated up, no evaporation, the entire water cycle gets affected , that’s why we get irregular monsoons, erratic monsoon season.
150 years is the life of atmospheric Carbon. 4200 metric tons of carbon dumped in the environment globally. For 150 years carbon dioxide can stagnate itself in the atmosphere.
More than 42000 million tons of carbon got dumped in atmosphere globally according to 2019 report.
1800 million tons of carbon dioxide gets recycled naturally. 1800 gets recycled naturally, rest gets stagnated and trap heat. Once the heat is trapped, the climate changes. Every level we give out exponential level of pollutants to the environment.
1972: Different nations gathered together in an international platform in Stockholm from 5th of June till 16th of June, the first event came in the protection of the environment when the early signs of climate changes were seen. If such kept happening the planet won’t be safe for living in the future. Weather is a smaller picture.
Picture of what is happening in planet earth. Climate on the other hand is a border picture.
Stockholm came with world environment day. The broader picture was changing.
Stockholm declaration: the first international environmental agreement. The declaration of world environment day on 5thof June.
The Nairobi declaration: Editor of Stockholm to improve strategies not well planned, finances went wrong. Lots of hypothesis came up.
First earth summit(1992): Action plan to cut down green-house gases to mitigate climate change disaster. Every nation should cut down by 5% of green-house gas as compared to 1990s level. 1990s was worst polluters decade. Every country had 20 countries to achieve this target.
Why nations were reluctant to accept this. Rule of environment. Echo of development is directly proportional to Resource consumption is directly proportional to Green-house emission is directly proportional to climate change. 1990 no one wanted to cut down on emission, every nation wanted to be super economy. The protocol was suppressed.
After 5 years (usually it happens after 10 years) United Nations understood the seriousness.
1997: UN requested nations to cut down on green-house gas emissions. The first warg summit was restructured.
Kyoto protocol: A developed nation has to cut down on more emissions that means cut down on greenhouse gas that means they have to compromise on resources by default they had to compromise in economic development. The developing nations has to do less. The developing nations have higher economic rate. It was blessing for developing nations but a threat at times developed. Developed countries had higher limit of emission control. Developed nations started investing in developing nations like India and the birth of globalisation took place. If any country is established in India the emission control limit becomes less. It changed the scenario throughout the world and the world became globalised. In fact, BPO, KPO and service sector is a result of service sector.
0% was the emission limit for India as India was agricultural based economy. Only after Kyoto proton and foreign investment
European and Canadian union started investing in India. SAARC nations received a lot of investment.
Due to globalisation there was peace and harmony, technological emissions happened.
Supplementary globalisation or trade liberalisation the net emission remained constant. When a developed country is investing in a developing country, it is getting subsidised emission limits. That means the amount of emission is not being cut down. The emission are going to the atmosphere.
Every nation take control of emission control. That is why Kyoto protocol is not very successful.
Every individual should cut down on carbon. Cutting down on carbon is not that hard.
Accident prevention, reporting, registration investigation and assessment.
History of bound laws.
Laws (International) Environmental
- Polluter base principle: any individual or entity or company creates damage then the entity has to pay compensation for the victims and for the restoration for the damage.
- Precautionary principle: To avoid permanent irreversible damage. Lack of in-certainty can be the reason for negligence.
- Principle of sustainable development: use that our future generation also gets to use it. Vellore Palar river has group of industries. Tanneries, paper mill are some kind of industries. A lot of waste water is generated. Waste water was collected at a common point and was discharged in the same river or in the agricultural lands. The waste water had a lot of chromium. So a case was filed against Vellore tanneries by union of India. It has 3200 bpm of BOD.
- Herbal tanning: organic
- Scrod tanning: Chromium has heavy metal, if it is a consumed by fish and then man, the man dies. It accumulates in a particular system.
Court implements the following in the order:
- Reversal of burden of proof: The person has to prove they didn’t do any damage. Pay compensation for restoration of the damage.
- Precautionary damage: Asked to establish effluent treatment plants. Contaminated of water body is taken in BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand).
30 BPM is recycled by nature itself.
Portal water: 5 BPM BOD
Contaminated but it can be discharged in the river or environment: Up-to 30 BPM
Unfit for drinking: More than 30 BPM
Taj Mahal: principle for sustainable development. Mathura was sealed and shifted outside.
Compensation is not always in monetary value sometimes through corporate social responsibility and social responsibility.
Increasingly BOD, algae happens which cuts off the oxygen demand for the aquatic plants and animals. The carbon dioxide cannot escape causing carbonic acid. Dilute the water before releasing.
All the industries use soap for cleaning which increases phosphate and nitrate in water because of which the microorganisms which need phosphorus consume it give bio products as carbon dioxide which creates foul smell.
Accident: Ammonium Nitranium disaster happened recently. Bhopal gas tragedy. Any man-made disaster can be mitigated. When disaster happens we don’t have sufficient technology to mitigate, we just have to run. Prevention is better than cure. Transport, social, industrial, nuclear classifications.
- Peace of mind while working efficiency and productivity will be good. Human is a social animal we work in groups, mobs and culture. Even a small panic can generate a lot of panic. We lose ourselves of our responsibility and land up into an accident. The small accident is mitigated and not converted into a disaster.
- We must be aware where are the protective equipment are placed.
- Work place training like mock drills to prepare for actual fire. One group hose pipe, one group for fire alarm.
- Don’t multitask (for electronics).
We can’t mitigate natural disaster. We can enhance our alertness time for minimum loss and minimum casualties.
Role of community in disaster
Emergency methods for carrying out casualty
Rescue operations in different types of emergencies- demonstrations
Fire- home safety, work place safety
Search and rescue (EMRC), evacuation & fire
A serious disruption of the functioning of a society, causing widespread human, material, or environmental losses which exceed the ability of the affected society to cope using only its own resources.
What is destruction and disruption?
Disruption: loss of human life. The environment is included in it.
Incident of fire: affects the env but if it affects humans it is
Increasingly BOD, algae happens which cuts off the oxygen demand for the aquatic plants and animals. The carbon dioxide cannot escape causing carbonic acid. Dilute the water before releasing.
All the industries use soap for cleaning which increases phosphate and nitrate in water because of which the microorganisms which need phosphorus consume it give bio products as carbon dioxide which creates foul smell.
Accident: Ammonium Nitranium disaster happened recently. Bhopal gas tragedy. Any man-made disaster can be mitigated. When disaster happens we don’t have sufficient technology to mitigate, we just have to run. Prevention is better than cure. Transport, social, industrial, nuclear classifications.
- Peace of mind while working efficiency and productivity will be good. Human is a social animal we work in groups, mobs and culture. Even a small panic can generate a lot of panic. We lose ourselves of our responsibility and land up into an accident. The small accident is mitigated and not converted into a disaster.
- We must be aware where are the protective equipment are placed.
- Work place training like mock drills to prepare for actual fire. One group hose pipe, one group for fire alarm.
- Don’t multitask (for electronics).
We can’t mitigate natural disaster. We can enhance our alertness time for minimum loss and minimum casualties.
Role of community in disaster
Emergency methods for carrying out casualty
Rescue operations in different types of emergencies- demonstrations
Fire- home safety, work place safety
Search and rescue (EMRC), evacuation & fire
A serious disruption of the functioning of a society, causing widespread human, material, or environmental losses which exceed the ability of the affected society to cope using only its own resources.
What is destruction and disruption?
Disruption: loss of human life. The environment is included in it.
Incident of fire: affects the env but if it affects humans it is
Variable:
- Causes: earthquake, food
- Frequency: fire are very often.
- Duration of the impact: Time of exposure. Longer the impact, more effect.
- Speed of onset: hazard into disaster. If slow it can be predicted and people can get ready for it. If it rains throughout it will cause flood.
- Scope of the impact: Richer scale for earthquake, speed for cyclone.
- Destructive potential: more scale higher impact
- Human vulnerability: we are trying to find extra territorial life but an invisible virus puts a hold on everything.
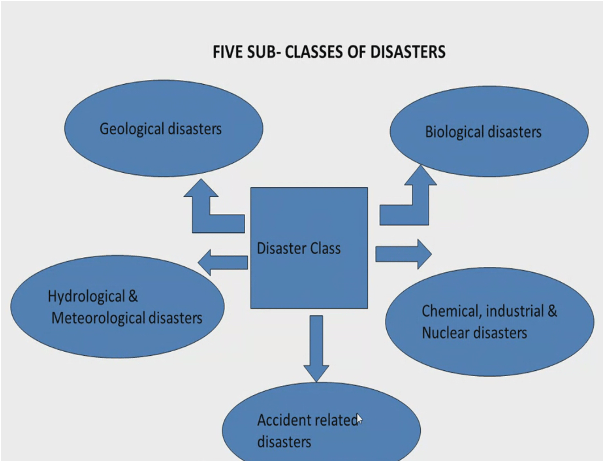
Anything in the animal and plants coming to humans is called as biological disaster. Like corona virus. The locus attack coming from Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Fire comes under accidental now. It can occur anywhere, so it becomes as accident.
Accident means sudden great loss.
Chemical, nuclear, radiological disaster: chemicals for fertilisers. What happened in Hiroshima.
Every disaster has effects and consequences. Although they are synonyms.
Walking through
2005, it rained in Bombay there was flooding. People were forced to use same water for cooking, eating, bathing, etc.
So they were thought how to use clean water.
Sickness due to drinking radioactive water:
Debris:
- People buried under.
- It blocks the road.
- No power supply, no water supply.
CBrN hazards: cover from head to toe. Plastic material or non-porous material used.
Lockdown self-imposed for 48 hours.
Stress: it is defined as the perception and assessment of the environment. This means that everything we see, hear, feel and smell is a source of stress, secondly since we ourselves are also a part of the environment that the way we think, our memories, ambitions and experiences are also a source of threat. It changes from person to person.
Children have 0 perception.
Senior adults have good perception but they are physically disabled.
Optimum Stress level ( OSL): It is the amount of stress. At which each individual functions most effectively is termed as optimum stress level. It is the capacity of the individual concerned. So as long as the stress is maintained close to the OSL it is the valuable and motivating. If it rises too high or falls too low then it will affect our behaviour.
People above 65 years have stress level more. They are asked to stay home.
Children below 10 years have stress level low. They are asked to stay home.
Negative stress level:
There is lack of enthusiasm for the task in hand. A feeling of depression and futility. A belief that nothing matters anymore and even the smallest task become difficult. Feeling bored and lack of energy. Find it very hard to summon up energy to start new job or create fresh initiative. It leads to mental confusion and physical anxiety. Inability to think effectively to remember instructions or trainings or to work out problems clearly and objectively. At high level panic may be dangerous choices and decisions to be made.
Bodily tension includes:
Rapidly breathing heart, high BP, excessive perspiration, trembling and feeling faint, churning stomach and indigestion, dry mouth, uneven breathing.
Positive stress level:
An alertness and self-confidence is created.
Think and respond quick and effectively.
Perform well and have feeling of enthusiasm.
There is interest in the task,
Strain
It is the internal response to stress. It acts in organisms produce strain.
An individual’s perception
I tension
Duration of exposure
Other stresses already present in the individual’s environment. Loss of income, loss of livelihood.
Stress, strain change in performance..further stress..further strain
| Stage | ||
| Stress | Accident caused by unsafe act, equipment or unsafe conditions | Element of surprise, aggressive |
| Change in performance | From cheerful to state of confusion | From confidence to surrender |
| Strain | Internal feeling : stomach turning over, tension and crying | Mind going blank, dizziness, sweating, rapid heart beat |
Disaster Management
A planned approach for the prevention of disaster, preparedness and response to disaster and recovery following disasters.
Search and rescue (EMRC), evacuation & fire
A serious disruption of the functioning of a society, causing widespread human, material, or environmental losses which exceed the ability of the affected society to cope using only its own resources.
- Surface casualties.
- Searching slightly damaged buildings.
- Searching likely survival points.
- Selected debris clearance.
- General debris clearance.
- Once survived form an ideal group of 8 volunteers as CERT (Citizen Emergency Response Team)
What is destruction and disruption?
Disruption: loss of human life. The environment is included in it.
Incident of fire: affects the env but if it affects humans it is
Variable:
- Causes: earthquake, food
- Frequency: fire are very often.
- Duration of the impact: Time of exposure. Longer the impact, more effect.
- Speed of onset: hazard into disaster. If slow it can be predicted and people can get ready for it. If it rains throughout it will cause flood.
- Scope of the impact: Richer scale for earthquake, speed for cyclone.
- Destructive potential: more scale higher impact
- Human vulnerability: we are trying to find extra territorial life but an invisible virus puts a hold on everything.
Anything in the animal and plants coming to humans is called as biological disaster. Like corona virus. The locus attack coming from Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Fire comes under accidental now. It can occur anywhere, so it becomes as accident.
Accident means sudden great loss.
Chemical, nuclear, radiological disaster: chemicals for fertilisers. What happened in Hiroshima.
Every disaster has effects and consequences. Although they are synonyms.
Walking through
2005, it rained in Bombay there was flooding. People were forced to use same water for cooking, eating, bathing, etc.
So they were thought how to use clean water.
Sickness due to drinking radioactive water:
Debris:
- People buried under.
- It blocks the road.
- No power supply, no water supply
CBrN hazards: cover from head to toe. Plastic material or non-porous material used.
Lockdown self- imposed for 48 hours.
Stress: it is defined as the perception and assessment of the environment. This means that everything we see, hear, feel and smell is a source of stress, secondly since we ourselves are also a part of the environment that the way we think, our memories, ambitions and experiences are also a source of threat. It changes from person to person.
Children have 0 perception.
Senior adults have good perception but they are physically disabled.
Optimum Stress level ( OSL): It is the amount of stress. At which each individual functions most effectively is termed as optimum stress level. It is the capacity of the individual concerned. So as long as the stress is maintained close to the OSL it is the valuable and motivating. If it rises too high or falls too low then it will affect our behaviour.
People above 65 years have stress level more. They are asked to stay home.
Children below 10 years have stress level low. They are asked to stay home.
Negative stress level:
There is lack of enthusiasm for the task in hand. A feeling of depression and futility. A belief that nothing matters anymore and even the smallest task become difficult. Feeling bored and lack of energy. Find it very hard to summon up energy to start new job or create fresh initiative. It leads to mental confusion and physical anxiety. Inability to think effectively to remember instructions or trainings or to work out problems clearly and objectively. At high level panic may be dangerous choices and decisions to be made.
Bodily tension includes:
Rapidly breathing heart, high BP, excessive perspiration, trembling and feeling faint, churning stomach and indigestion, dry mouth, uneven breathing.
Positive stress level:
An alertness and self-confidence is created.
Think and respond quick and effectively.
Perform well and have feeling of enthusiasm.
There is interest in the task,
Strain
It is the internal response to stress. It acts in organisms produce strain.
An individual’s perception
tension
Duration of exposure
Other stresses already present in the individual’s environment. Loss of income, loss of livelihood.
Licensed heart saver
Patient needs immediate help.
Duties, roles: scenes is safe
Breathing normally no CPR
Diabetes
First aid: Immediate care before more advanced training. First aid for life threatening too
Epithernine
- Responsive: speaks, moans and moves. Give pain and verbal stimulus.
- Unresponsive: doesn’t move or react
Tell you are a first aid provider
Call local EMS number
Patient breath:
- Scanning for breathing or not (chest is moving). If patient is not breathing perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation.
- Look for injuries/bite marks/medical information jewellery if patient is breathing. If patient is moving like moaning, groaning, etc. In India, ask relatives for medical history. Put patient in optimal position. To make the airway flow smooth.
- Confused/can’t answer assume he wants help
Restock after the emergency
American heart association heart saver
- Access the scene: be aware of danger for anyone nearby
- Move only if the area is dangerous
- Phone for help your self if none around, if someone is around call yourself.
- Tell how to get to you
- Send one to meet the paramedics
911:
- Doesn’t respond to voice or touch.
- Received electric shock
CPR/
EMS: Emergency Medical service
Maharashtra is 108. It is state toll free number.
If we get blank we should call on EMS number.
Give medication under a physician.
Suppose the ambulance will take time, can we ask the physician to give medicine over call?
Sorbitrate is dangerous
Aspirin
Make the patient calm
Make room ventilated.
Protective gloves:
No one should be exposed to blood and body fluids
Wash hands properly with warm water and soap for 20 seconds.
Use hand sanitiser
- I will now dispose protective glove now
- Inside out
- Cup it
- Dispose to biohazard bag
Don’t pinch, but tap on their shoulder
- Pelvic or spine injury
- Move if the person is injured if area is dangerous
- Drag the person by his clothes.
- If person is unresponsive, move him to the side this helps open the airway.
- Keep private information private. Only share medical information with medical staff.
- Call EMS so more experienced people can take over.
Optimal position: turn left side or right side.
Before handling any patient wear personal protective equipments. Gloves, mask, gown, board, eyewear.
Use sanitiser and dispose of gloves in a safer place.
Difficulty breathing/choking
Make sure scene is safe
Ask for help if person is sweating.
Ask if medicine is needed.
Call 911 if breathing gets worse or person becomes unresponsive.
Give CPR if person is gasping.
Speaks no more in between breath
whistle sound
Asthma
patients carry inhaler medicines.
Don’t give inhaler if the person is taking it for the first time. Make him sit and not stand as it makes breathing difficult.
Inhaler: shake it, attach spacer if available.
Ask the patient to sit.
Tilt his head back and ask to blow out slowly. As blowing fast doesn’t reach the lungs.
Push down the medicine vanished
Hold the canister for 10 second.
Breathe deeply
Pause for some time and then release
Inhaler devices:
Partially blocked: partial blockage in airway
Completely blocked: no energy and exit of air.
Give thrust above the belly.
Fist in front, below breast
Make a fist, put thumb above belly and below breast. Give upper thrust.
It person is large put arms under the arms.
Mild: cough loudly
Tough: can’t breathe or talk.
If chocking adult becomes unavailable call 911. Provide CPR if needed. After 30 compression. If u see object in mind, take it out. Don’t take blind sweep.
2 breaths, 30 compressions.
Perform until someone more experienced takes over.
Choking in children:
Blocking in airway.
Mild: coughing
Severe: can’t talk, or speak
Give thrust slightly above stomach
Each thrust pushes
Go to the level of the child.
Stand behind the child. Locate belly button. Upward thrust. Repeat until
The child can breathe.
If unresponsive.
Shout for help. Get an AED. Put on speaker mode. Check mouth for object after each set of
Compression.
Use AED as soon as it is available.
Choking in Infant (1 month – 1 year)
They turn blue when they are chocking and they won’t cry. They won’t even breathe.
Sit on chair
Turn infant upright
Give 5 backslaps
Turn to back, use two finger and push for the same area for CPR until he is responsive. Give chest thrust.
After that take to health care provider.
Don’t give thrust on abdomen.
Keep infant on table and shout for help. Go with CPR along with give two breaths. Don’t go for blind sweep, it can ruin the inner lining.
Check mouth for foreign object.
Use AED as soon as it is available.
Mild and allergic reaction
Stuffy nose
Sneezing
Itching around eyes
Itchy skin
Running watery eyes
Running nose
Rash
Hives
Epinephrine injection: spring activated.
Halfway between hip and thigh. Don’t put finger over the area. The person should rub the area for 10s.
If there’s delay in help by 10 min give second shot of epinephrine.
Call someone to call 911.
Shock
Trouble breathing
Auto injector
Epi-pen.
Insulin pen. Load it and put it over the skin of the patient. Load the dose and put it at the lateral (outside) portion of the patient. In between the knee and the hip joint. Hold for 10-15 minutes and then ask the person to run it for 10-15 seconds.
Heart attack
Many people with uncomfortable feeling at the centre of chest (squeezing, uncomfortableness or pain). Jaw, back or neck pain. It is the most kind of medical emergency. Majority land up into cardiac due to heart.
Breaking in cold sweat, light head was.
Difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack:
Heart rhythm is unstable or abnormal not sufficient enough to pump the blood. Hypoxia: low oxygen in body. The patient is unresponsive and not breathing. Stop the abnormal rhythm. Compress the chest to get back to normal breathing.
Heart attack:
Blood flow is blocked. Heart requires blood and glucose.
Muscles not getting nutrients and blood.
If blocked vessel is not opened.
Heart attack can lead to heart attack.
First aid and AED
don’t want to believe they have a heart attack. The first few minutes of heart attack are most important.
Chest feels tight.
Call EMS.
Call first aid kit and AED.
Sweating a lot and nauseated.
Ask for bleeding, stroke.
Tell address to reach.
Loosen up the clothes.
Give adult dose aspirin (325 mg/1 tablet) or 4 low baby dose aspirin (75 Mg) if not allergic under medical supervision. Chew it up swallow. The absorption happens from the mouth. If there’s bleeding in blood don’t give aspirin. It acts blood diluter and blood thinner.
Don’t give aspirin if they have had surgery.
Seizures
Seizure are jerky movements and involuntary. Frothy mouth in some cases. The whole body becomes stiff and hard.
Steps:
Ask if Okay
Put the phone in speaker mode call EMS
Get first aid kit
Give address
Warning signs: arm weakness, face drooping, slurred speech. Call EMS.
Be with person until more trained person comes
Don’t put anything in mouth when they are having seizures to clean the frothing. They will have lock jaw. As sometimes they bite.
Seizure is caused due to epilepsy, heat related, cardiac arrest, poisoning, low blood sugar.
Seizure stopped, moving but not responding
Give first aid after the seizure is over.
The person can fall asleep after seizure.
Move foreign objects.
Move towel or something soft under the patients head.
If gasping/unresponsive provide CPR.
If person is vomiting or having fluid in mouth, turn to right.
If bleeding is from mouth, cheeks, put pressure with gauze after wearing gloves.
From sad news
Gets dizzy and becomes unresponsive.
Make sure scene is safe
Call EMS if person becomes unresponsive.
If person fell look for injuries
Don’t give something to eat if person is unconscious. If the patient is conscious give something to eat or drink.
It is a reversible process. If person faints for more than 2 minutes take to the doctor.
Diabetes
Insulin is needed to maintain
Low blood sugar
Hasn’t eaten
Or had enough insulin
Oral glycemic tablets
If they take tablets without meals.
Can become irritable, confused, sweaty, can have seizure
Give something with sugar in it.
If person can sit up and swallow ask
Person
To have something with sweetness.
If person can’t don’t force let them sit peacefully.
Call EMS if person is unresponsive.
AED: Automated external defibrillato
Stroke:
Burton’s aren’t getting blood supply.
FAST
Facial symmetry: the left side and right side are asymmetric
Drooling of saliva
Ask the patient to hold the hair in the air
Affected side will have loss of power and sensation.
Time when the person was seen last normal.
Injury emergency
Clean the area up before someone gets hurt. Make the scene safe.
Tell them you took first aid course
Get first aid kit and apply dressing.
Put cotton on bleeding area.
To stop bleeding press on hard through gloves apply direct pressure on the bleeding site.
Don’t pull out gauze as it might the blood stick to it. Put another cloth over the first one.
Put pressure till the bleeding stops.
Dressing: clean material directly over wound.
Bandage: protect or cover injured body part.
Tourniquet two inches above the cut/wound. Pressure will stop the further flow of blood. Complication is loss of blood to the other part can get
Lecrosed.
Write time of the
Windlass : to tighten
Internal bleeding
Dryness of mouth take to EMS.
Have the person lie down.
Provide CPR if needed.
Concussion head injury.
Brain moves inside the skull.
Confusion, loss of memory, loss of vision,
head and spine injury don’t move
String blow to head
Injury during driving or biking
Helmet broke in a crash.
Other than concussion may not move.
Change in consciousness.
Call EMA if the person loses consciousness.
Spinal injury
65 years or older
Tenderness in back
Appears not alert
Don’t twist or turn the head
Only when CPR is needed, has fluids in mouth
First aid kit and AED.
Sprain:
Straining ankle
Make sure area scene is safe
Cover Open wound
Apply something cold (ice and towel for for 20 min)
Stay off activity for a while will help with swelling.
Sprains often occur in the following circumstances: Ankle — Walking or exercising on an uneven surface, landing awkwardly from a jump. Severe pan, painful mobility movement, restrict movement of the fractured site.
Apply strain spray like Volini, Moov.
There’s discontinuation of the bones.
Broken bones
Apply splint to an injured arm. Prevents an injured part from moving. Injury needs to be protected.
Should support the area above and below the injury.
If u use something hard as a splint use something soft to cover it. Splint between two joints.
Head injury
Ringing in ears, blurring in ears, altered mental status, head ache.
Limit the mobility of the head.
Be very careful while carrying the patient over to the stretcher. It can cause life time paralysis. Don’t manhandle the patient. Be very careful. Restrict the motion as far as possible.
Don’t gather a huge crowd.
Burning
Two types are superficial and deep burns. Superficial are very common like ironing, cooking. Main Management is just to wash with cold water and put sterile cloth. If tissues are burnt it can be life threatening.
If deep extinguish the fire.
Take wet blanket stop, drop and roll. Don’t remove the jewellery stuck to the skin. Inform the burn centre to manage the burn. Infection is high in case of burn. Apply sterile dressing over the area.
Apply something cool to the area but not ice cold.
Use cool freezing compress until it doesn’t hurt
If burn area is large call EMS
Remove clothes, jewellery not stuck to skin
10 min put running water
Cover with dry blanket
Check for shock
Healthcare provide can determine if additional treatment is necessary.
Electricity
Turn power of ur trained
If off touch the person
Marks visible of electricity
Can cause abnormal heart rhyme and cardiac heart arrest
Wear PPE
Contact EMS
Provide CPR
If due to high voltage due to fallen wires call EMS and inform the concerned authority.
Heart is having its own electrical activity. Movement of the heart will become abnormal. Stop Fibrillation
To make sure the heart is moving in a rhythm.
Resuscitated if high quality CPR is taken.
Bee bite
Remove the stinger.
Don’t burst the poison bag which can cause itchiness. The bee’s posion bag is acid and the soap is base.
Wash with running water and soap.
Keep ice bag and towel.
Animal bite
Immediately stop bleed
Wash wound with good amount of water
Call EMS
Snake bite
Make sure the scene is safe
Don’t catch/hurt the snake
If half killed, it still can bite
Common in rural areas.
Majority of snakes are non-poisonous,
They can be classified according to colour and size.
Make the person calm as panic leads to cardiac arrest.
Remove through Tweezer
Take tick in a plastic bag
Don’t cut the bite site
Don’t suck the blood
Don’t tie something tight
Jellyfish/Marine bites
Make sure scene is safe
Remove off stinger inside skin and tentacles with gloves
Use vinegar/baking soda and water
Take shower with hot water for 20 minutes
Call EMS known to have poisonous marine animals of the person has medical emergency.
Heat emergency
Be hydrated
Dehydration can lead to shock due to diarrhoea, excessive sweating. Give something to drink to water.
Dru mouth
Dizziness
Less urination than usual
Heat cramps
If dehydration is not corrected it can lead to heat cramps which can lead to head shock.
Painful muscle spasms
Headaches
Make sure scene is safe
Wear PPE
Have the person rest and cool
Have something sugar and electrolyte
Bag of ice for 20 minutes
Follow gradual cooling the person by Cool water spray or immerse in water
Don’t keep cooling, it might lead to low cool body temperature.
Put cool compression under arms, groin
Give sports drink water
Signs: nausea, fatigued, heavy sweating, dizziness
Provide CPR if needed
Frostbite
Appears at a local area like hand, feet etc. It can lead to nephrosis of the cells.
Cool gases
Skin is white, waxy
Cold, numb
Skin doesn’t move when u push it
Move person to a warm place
Remove wet clothes
Put dry clothes on
Remove tight jewellery from frost bitten part
Don’t cut the frostbite area
Don’t rub be gentle.
Hypothermia: low body temperature. Can be even if the temperature is above freezing
Sleepy, confused, ice cold skin and blue like a dead body, stiff
Turn on room blowers and heaters
If unresponsive provide CPR
Get to medical care as soon as possible
In India, it’s a tropical climate so we don’t have much of cold-related conditions.
Poison
Make sure scene is safe
Leaking containers stay away
Look for multiple people who might have been poisoned
Give only the antidotes told by the poison centre
Safety Data sheet has recommendation
What is name of person
Poison intake
Weight of person
When did it happen
How is the person acting now
Age of the person
Safety shower and eye wash area
Remove jewellery in touch with poison
If eye is affected ask him to blink as possible while rinsing the area
If one eye it should be at a lower level.
CPR
Heart attack takes more life than all the cancers included.
Scan chest for 5- 10 seconds
Remove clothes and practise CPR
If someone is breathing, their heart is pumping don’t give a CPR.
CPR is for abnormal rhythm or not pumping heart
30 compressions and 2 breaths. Continue for 2 minutes at a stretch : 5 cycle of CPR
ADR will analyze the rhytm
Press the shock button and give EPR
Do till the EMS arrives or patient is responsive