Skills needed
Insights to business organization and activities, different business function, concept to organizational behavior: dealing and managing people, how to effectively manage things, dynamic business scenario and what skills needed to acquire to do business effectively.
Group and individual presentation. How do you work in teams? Some individuals don’t perform well to know the strength and weakness.
Challenges: ethics, change management, global, impact of change on stress, five important managerial function, type of decision, decision style, planning.
organization structure: how does it affect, group formation, how to measure the performance and standard, individual behavior, leader and normal people behavior, communication, transaction analysis, why is motivation necessary, leadership and theory and how it evolved, controlling as a function is important tool for measuring organization performance.
What skills should managers acquire:
Sholey: Old wine in a new bottle: different perspective
Learning 1: If you can’t do it yourself. When Jay and Veeru is out of jail Thakur is waiting. He is waiting for them to catch them alive. As he can’t do it himself. Outsource. If you can’t do it yourself, you can ask someone else to do it for you.
Learning 2: Team work. Be together in each and every task. You cannot always work in isolation. When you are going to work with a group of people you interact with people with different upbringing, family history, educational background, ethics etc.
Learning 3: Baseless claims put you in trouble as when you are interacting with customers outside the organization, they assume you are talking on the behalf of the organization. Never over-commit as it will affect the goodwill of the organization and as well as an individual.
Learning 4: Whenever you go for negotiation and you see it will benefit the team always do an evaluation. It is called feasibility: economic, technical and see if you have resources to complete it on time. Also know the return of investment. Just because you are going to get benefitted blindly don’t expect you need to do a careful evaluation.
Learning 5: Self-delusion: carrying a wrong impression about yourself. It is a dangerous thing. Undergo a SWOT analysis of yourself to know our strength and weakness, opportunities and threats. People are always observing you as you will immediately get lost. Reflect what you are so they accept you as they are. If someone can’t understand you that means you aren’t reflecting your true self.
Learning 6: In the organization when you communicate what do you need?
You need network and right source. We need to know what is authentic and reliable source. The information should be from a reliable source and accurate. Then we can give information to the audience according to the preference. Avoid jargons and use simple English.
Learning 7: Grapevine means rumors. Everyone working at an organization is exposed to a grapevine at some point or the other. Organization after pandemic: reduction from workforce,
Always the authenticate the source, such information has to come from the HR or reliable source. Multi-organization has people different levels as spies hence refrain from:
- When you go to tapir never talk about the organization.
- At the party don’t discuss about boss or organization
- Never discuss anything in the bus.
So, anything casually said can be reported to higher authority.
Learning 8: People have certain skills that is why they are in the organization. Have a discussion with the team member, understanding the strength and weakness so you know when to give task, don’t ever be partial where you allot of work to an individual person, during performance appraisal do it purely on basis of their performance. If you respect and understand your team you will get respect. You always earn respect through your actions. When you respect people, your team will always stand for you.
Learning 9: Don’t carry work home as people get irritated. Devote time for you
HR policies: picnics, recreational facilities, fully equipped gym, brain storming sessions, smoking room. If an employee mind is not fresh, he might not be able to work efficiently.
Learning 10: When you are interacting with the superiors and with outside the organization you accept the limitation but accept that you need time. When you are selling yourself be truthful.
Learning 11: Go to the extreme level. We do everything according to Standard of Protocol still things get wrong. Suddenly client goes with unrealistic deadline: lack of resources and time. You might need to take extreme steps. In spite of proper planning things get out of control so you need to take extreme steps.
Learning 12: Opportunity strikes once. You should know where to grasp that opportunity.
Learning 13: Whatever task you commit for make sure it is of expected quality.
ISO certified.
Learning 14: When you are actively engrossed on a task you will come to opportunities. Be on a lookout for certain situations to understand what opportunities lie in store.
Learning 15: Stay alert! Be aware of your competitors. When you’re in control something can go wrong. Capture information to know what is happening in the environment.
The captain.
Learning 16: Take out time for your hobbies and passion. All work and no play, makes the ravines a dull place. Don’t always concentrate on work also enjoy life. Mind needs to be fresh and rejuvenated.
Learning 17: Never make half baked jobs. It makes the work out of hand. Always complete the work on time.
Learning 18: Never show all your cards. Never reveal yourself to your customer or client completely. Don’t put everything in front of the client as the negotiation might not go as planned. This is more with people when you are interacting with someone outside the organization. Be very clear with your team be very clear with them. Once you gain their trust slowly reveal yourself.
Tata motors are pioneers in the market especially in the heavy wheel. They planned to launch Tata Indica. Dealers were overbooked, lots of cancellation as people had to wait for 6-8 months for the car. The lucky customers found the quality wasn’t worth it: the interiors, the clutch, the tyre wore out after 10,000 kms.
Inception, growth, maturity and decline
Maturity: Success or benchmark. Once you reach success maintain the quality. Don’t towards the decline.
How to avoid data breach?
If we are very clear and transparent with our team mates what we want they might share the strategy with the other people outside the organization and the idea can get stolen?
Confront the person and according to their response contact the higher authority.
What do managers actually do?
Google found it difficult to deal with everyone’s problem as everyone had different problems.
Engineers didn’t want micromanagement but they like implement management.
Does a manager actually matter in the company does it matter?
Google are A level employed people. They know job. They didn’t want to be directed by anyone.
- Background
- What are the issues that the engineers or the managers faced so that manager has to take particular decisions.
- Findings : Lot of chaos as there was lack of managers.
What is flat system?
There is no top level management. There is no hierarchy. It is easier to approach everyone, faster communication and getting things resolved quickly.
Initially in Google:
- Working system had flat system.
- 360 degree feedback : self evaluation from everyone. If there is any problem in dealing with people in organisation. People in Organization take some time to develop career wise and personality wise. They could convince the engineers why management was necessity.
Story :
Lion is sighing lazily enjoying his day. The fox asked the lion what time it was as the watch was broken.
Lion has big paws and he would destroy more. Lion said he would fix it. Fox thought it was ridiculous.
Lion was very adamant that he could repair.
Lion comes back with the watch repaired.
Wolf comes and says his TV set is broken. Lion says he can repair.
Wolf doesn’t believe it. Lion convinces him and lion comes back with TV.
Inside the cave, the rabbit are doing work.
Lesson :
If you want to know why a manager is famous look at the work of his sub-ordinates.
Why someone undeserved is promoted as his sub-ordinaries are good. Some people are not good at work but they know how to get work done from others. That is the primary role of a manager.
Sometimes the sub-ordinaries need to be put in pressure by giving deadline.
Story : Rabbit is typing on his type writer, rabbit says he is working on thesis. Rabbit is work king on how rabbits eats foxes. Foxes find it ridiculous. Rabbit takes him to den and comes back with Fox bone.
Wolf comes. Same happens with bone.
Bear comes and asks.
Lesson : it doesn’t matter how silly your thesis topic is, what matters is whom you have as a supervisor.
It doesn’t matter how bad your performance is, what matters is whether your boss likes it or not.
Manager is taught not to be biased. Then brainstorming sessions happens. The managers are very open and transparent.
Learning outcome :
Describe the functions
What is an organisation
Why is the structure important
First line manager :
- It differs according to the industry.
- Manufacturing industry :
- Shift supervisor : Whatever work has been assigned to the worker is done on time, as per it is done. The project manager needs to have a project management plan in mind. How much to be alloted which member. They act as a link between middle level management and the workers below that. They try to understand the problem and solved it. If they can’t resolve it it goes it middle line managers.
- Middle line manager: Departmental Head.
- They make the work of first line managers easier.
- Un-skilled and skilled.
- In IT industry it is Project leader.
- If there is a policy framed at the top level. They have multiple process heads under them. He tells which tasks to be done, budget allotted, timeline, etc.
- Top managers: Individuals who are responsible for the success of the organisation. Top CEO.
Https://www.catalyst.org/research /women-in-management/
Women are much emotionally stronger than men, they have better understanding than men and therefore they make better decisions. In top fortune companies women are in top management.
Top-down approach :
- Top managers
- Middle managers
- First line managers
- Non-managerial employees

Bottom up approach :
If the bottom people can’t make decision they refer to people on top of them.
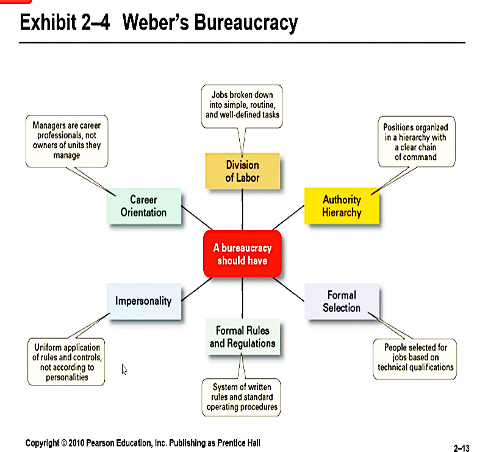
What is management ?
- Efficiency: Doing things right.
- Effectiveness: Doing the right things. Attaining organisational goals.
How to apply for leave irrespective of what-ever reason?
Ethics: Listen to other person in the group. Managers job is to socialise more.
Hawthorne studies/experiments (1920-1930) :
- Understanding human nature
- Factors affecting human nature
- Illumination experiment : effect of productivity of illumination. It doesn’t affect on individual and type of work.
- Relay assembly test room study (1927-1929) : In supply chain and manufacturing people aren’t given break according to their preference. Flexibility in giving breaks increased the productivity.
- Mass Interview Program :
- Bank wiring Observation Room Experiment(1932) : 14 male workers in the bank wiring room were placed under observation for six months. A worker’s pay depends on the performance of the group as a whole. The researchers thought the efficienct workers would put pressure on the less efficient workers to complete the work. The most efficient workers feel why should I work when others reap the benefits.
- Social and psychological factors : Only physical working conditions are not enough to increase productivity. Their emotional well being depends on it. It is responsible for productivity and job satisfaction.
- The informal relations : Informat relations matter more than formal.
- Employees will work better if they are allowed to participate in decision making affecting their interests.
- They will work more efficiently when they believe the management is interested in their welfare.
Open systems and close systems
Input :
- Raw materials
- Human Resources
- Capital
- Technology
- Information
Transformation process :
- Employees’ work activities
- Management activities
- Technology and operations methods.
Implications of the systems approach :
Since external environment is dynamic.
The contingency approach :
Every time we can’t follow the rules laid down. Situations which we don’t anticipate makes organisation change their ways to sustain.
Through softwares and hardwares the organisation can make sure the person is working for 8 hours.
That change something of a similar nature I can always rely on decision we also discussed about more info all these things he said these problems can be completely I’m very defined you have all the information which is required understanding the problem.
As programmed in decision it means that decision is occurring very frequently or decision has to be made very frequently there is a standardized approach or a structured approach to anybody give me an example of a repeat it a decision. what’s all this open and decision it means that the decision is occurring very frequent your decision has to be made very frequently there is a standardised anybody give me an example of a repeat it a decision. What do you mean by Procedure, rule and more do you mean policy.
Unusual information
Decision making decision
Specific goals : Covering time period.
Why do managers plan?
Planning provides a direction.
Avoid uncertainity
Goal setting
To help focus your answers, think of at least three categories of life goal:
- Relationships with other people (family, friends, work relationships)
- Work or career goals.
- Other person achievement activity goals (hobbies, travel, athletics, etc)
Part 1: 1 minute card one:
How do you want to spend the rest of your life? Make a list of activities and goal for your life.
- I want to have a Notes ring relationship with other people where they understand me and I understand them. There is respect between us. There are no worries and everything is peaceful.
- I want to be well-established and well recognised from my name only.
- I want to explore different parts of area I want to be a swimmer.
Part 2: 1 minute card two:
What do you want to do the next 5 to 10 years? Again list activities and goals.
- Being a well-established company at a high-level.
- Smooth relationship with people. Make as much connections as I want.
- Want to be the most knowledgeable person. Explore maximum areas blog about it, explore the eateries and blog about it.
Part 3: 1 minute card 3:
If you have six months to live how would you spend at least three activities and goals
- I will tell them how much important they were in my life and how much they mattered to me. Whatever they needed I would have provided to them.
- If I was at a very high level I would have promoted people I would have given them recognition and importance. If I was still learning I would learn and try to impact as many people as I could. I would leave a mark for my name.
- I would like to spend maximum time with my loved ones to make memories with them.
Part 5: 1 minute card four, number one:
I want to have a nurturing relationship with other people where they understand me and I understand them. There is respect between us. There are no worries and everything is peaceful.
Part 6: 1 minute card four, number two:
Select the coal or activity from card to that you desire to achieve and write it here:
Being a well-established company at a high-level.
Part 7: 1 minute card four, number three:
I will tell them how much important they were in my life and how much they mattered to me. Whatever they needed I would have provided to them.
Part 8: 3 minute card five:
Right is the meeting said you could do in the next seven days to further your goals in God for. Do not evaluate the feasibility, brain Storm anything you can do a big in the next week and just ride in the parti.
Reach out to more people.
Initiate conversation with them.
Hang out with them and explore different areas.
Share resources with them and ask for suggestions.
Without any fear openly share my feelings.
Without being charged share my emotions and bond with them through it.
Part 8: 1 minute:
Scratch out any item on card 5 that you don’t actually think you can do or don’t intend to do.
Part 9: 1 minute cards six:
Choose three items from card five that you will do in the next seven days and write them on this.
Have a nurturing relationship with my love ones and understand them. Create respect.
Goals nothing but the objectives an individual wants to achieve.
Types of goals
- Financial goals:
Related to expected internal financial performance of the organisation.
- Strategic goals:
How related to the performance of the firm relative to factors in the external environment (example competitors). Apply to the entire organization. Establish the organization’s overall goals. Seek to position the organization in terms of its environment. Like releasing an advertisement it all depends upon the external factors. A lot of pre-planned even takes place so it is a well thought of before achieving something specific goal. Hence a lot of preplanning is needed.
- Operation plans:
- Specify the details of how the overall goals are going to be achieved.
- It has a shorter time period.
- Long-term plans
Plans the time frame extending beyond three years.
- Short-term plans:
Plans for timeframe of one year or less
- Specific plans:
Plans at a clearly defined and leave no room for interpretation. For example when the surgical strike happened in 2016 is an example of specific plans. The goal was pretty clear, the target was identified, the team was identified and the team was clearly knowing the role in the team.
- Directional plans:
- Flexible plans that set out general guidelines and provide focus, yet allowed discretion in implementation.
- The surgical strike was well planned but something goes wrong at that point of time the general guidelines need to be changed.
Types of plans:
Single use plan:
A one-time plan specifically designed to meet the need of a unique situation.
Standing plans:
Ongoing plans that provide guidance for activities performed repeatedly. Instructions given during research. Preparing for interviews.
Setting goals and developing plans
Traditional goal-setting:
- Broad goals are set at the top of the organization.
- Goals are there in broken into sub goals for each organizational level. Assumes that the top management knows best because they can see the big picture.
- Goals are intended to direct, kite, and constrain from above.
- Goals lose clarity and focus as lower level managers attempt to interpret and define the goals for their areas of responsibility.
The downside of traditional goal-setting:
- Top management is objective: we need to improve the company’s performance
- Division managers objective: I want to see a significant improvement in this divisions profits.
- Department managers objectives: increase profit regardless of the means
Setting goals and developing plans
Maintaining the hierarchy of goals
Means –Ends Chain
- The integrated network of goals that result from establishing a clearly defined her a key of organisational goals.
- Achievement of lower level goals is the means by which to reach high-level goals (ends): when you have something larger than life you always need to start from the bottom of the pyramid, so it’s a step-by-step process. From lower level to higher level one keeps progressing. Why does one need to achieve lower level goals than high-level goals.
Management by objectives (MBO)
Specific performance goals are jointly determined by employees and managers
Progress towards accomplishing goals is periodically reviewed .
Rewards are allocated on the basis of progress towards goals.
Key elements of India:
Goal specificity, participative decision making, and explicit performance/evaluation period, feedback. Based on the feedback the rewards are allocated.
Tips on a typical MBA program
- The organisations overall objective and strategies are formulated .
- Major objectives are allocated among divisional and apartment units.
- Unit managers collaboratively set specific objectives for their units with their managers.Concept of participative departments.
- Specific objectives are collaboratively set with all department members. Is there a set of objectives the department has to achieve it is very important that the objectives need t
- Action plans, defining how objectives are to be achieved, are specified and agreed upon by managers and employees.
- The action plans are implemented.
- Progress to words objectives is periodic Lee reviewed and feedback is provided.
- Successful achievement of objectives is reinforced by performance-based rewards.
Why MBO is success
Sometimes the top management frames a policy and expect the lower management should do things to fulfil those policies but you will find that there are less amount of commitment from the top management. One of the primary reason why MBA successful because they sit with different managers at different levels in order to set the goals that is equal involvement and commitment throughout the process right from action plan implementation feedback achievement of the goals in all the activities that the top management is involved in. So automatically the people. So that is one of the primary reason for the success of MBO. But we also need to Anna We also need to understand what kind of problems come if we follow this kind of path. Course and depending on the situation there are priorities which might change. Sometimes you might want to go back and revisit a particular call and say that this is what I cannot achieve, this is what I did, this is what I can achieve or something I might leave. We are living in a dynamic environment. When we are talking about organisations and their functioning in, it becomes absolute necessity that we need to come revisiting the goals and resetting the goals. If you’re following 70 following certain guidelines that this is the way ie done. But every time it is not possible due to the dynamic change in the environment so people see it as the petition to the problems that might come if you’re following in India.
When will it team successful?
The team will be successful when each and every member contributes to it. People for see to it that there is a load of verses on individual accomplishment, because unless individuals were assigned specific task don’t complete the work, the teams objective is not fulfilled.
Since over-focus on an individual‘s achievement, it may create problems for the team.
There are certain certification boards like music Amma, six Sigma, I SO. Some organisations under the MBO might not follow the actual MBO it is just on the paper that we follow this process but actually, it is not done as it has to be practice. To practise in all the eight steps have to be followed. People feel that they might not be actual commitments from the top-level management and it will just create a sort of paperwork. Ultimately the colonisation is not getting the benefit.
Well written goals
Written in terms of outcomes, not actions
- Focuses on the ends and not the means.
Measurable and found to be able
- Specifically defines how the outcomes is to be measured and how much is expected
Clear as to time frame
- How long before measuring accomplishment.
Challenging yet attainable
- Locals do not motivate.
- High goals motivate if they can be achieved.
Write down
- Focuses, defines and make schools feasible
Communicate all necessary organizational members
- Put everyone on the same page.
Difference between MBO and MBE
| MBO | MBE |
| It is an approach that involves defining the objectives with an organization involving the management and the employees. | It is an approach in which any deviation from the expected results is looked upon by the managers. |
| It is a management approach | It is a method of control. |
| It takes into consideration the plan of action in its entirety. | It is reviews only the expectation from the expected results. |
| Managers in MPO invite the views of their subordinates to establish the objectives | Managers in MBE get involved with the subordinates only when the latter unable to meet the objectives. |
| Policies and processors a set an than people are expected to follow them to achieve the objectives. | MBE sometimes require managers to take actions outside in normal policies and procedures to achieve a certain objective. |
Steps in goal-setting
Review the organisations mission statement.
Developing plans:
- Contingency factors in a managers planning
- Managers level in the organisation
- Strategic plans at higher level
- Operational plans at lower levels.
Degree of environmental uncertainty
- Stable environment: specific plans
- Dynamic environment: specific but flexible plans
Length of future commitments
- Commitment concept: current plans affect future commitments must be sufficiently long term to meet those commitments.
Approaches to planning:
- Establishing an informal planning department
- A group of planning specialist who help managers write organizational plans.
- Planning is a function of management, it should never become the sole responsibility of planners.
Involving organisational members is in the process
Plans are developed by members of organisational units at various levels and then coordinated with other units across the organisation.
Contemporary issues and planning
Criticism of planning:
- Planning may create rigidity
- Plants cannot be developed for dynamic environments.
- Formal plants cannot replace intuition and creativity.
- Planning focuses managers attention on today’s competition not tomorrow survival
- Formal planning reinforces today’s success, which may lead to tomorrow’s failure.
- Just planning isn’t enough.
Effective planning in dynamic environments
- Develop plans that a specific but flexible.
- Understand that planning is an ongoing process.
- Change plans when conditions warrant.
- Persistence in planning eventually pay off.
- Flatten the organisational hierarchy to foster the development of planning skills at all organisational levels.
Organisational structure
Purpose of organising
Divide is work to be done into specific jobs and departments.
Assign stars and responsibilities associated with individual jobs
Coordinates to words organisational task
Cluster job into units
Establish is relationships among individuals, groups, and departments.
Establishes formal lines of authority
Allocates and deploys organisational resources.
The degree to which stars in the organisation are divided into separate jobs at each step completed by a different person.
Over specialisation can result in human this economies from boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increase absenteeism, and high turnover.
Departmentalisation by type
Functional
Most examples are related to manufacturing industry. Under the plant manager there are manager, engineer accounting manager, manufacturing manager, human resources manager and purchasing manager.
advantage:
Efficiencies from putting together similar special loyalties and people with common skills, knowledge, and orientations.
Coordination within functional area
In-depth specialisation
Disadvantage:
Poor communication across functional areas.
Limited view of organisational goals.
Geographical departmentalisation
Vice president for sales: sales director of western region, sales director of Southern region, sales director of mid-western region, sales director of Eastern region.
Advantage:
More effective and efficient handling of specific regional issues that arise.
Serve needs to be unique geographic markets better
Disadvantage:
Duplication of functions.
Can feel isolated from other organisational areas.
product department lies Asian
Advantage:
Allow specialisation in particular products and services.
Managers can become experts in their industry.
Closer to customers.
Disadvantage:
Duplication of functions
Limited view of organisational goals.
Process departmentalisation
Plant superintendent: sewing department manager, planning and milling department manager, assembling department manager, lecturing and sanding department manager, finishing department manager and inspection, shipping department manager. Advantages more efficient flow of work activities. The disadvantage is can only be used with certain types of products.
Customer departmentalisation
Director of sales: manager, retail accounts, wholesale accounts manager, government accounts manager
Advantage is customers needs and problems can be met by specialist and its disadvantage is the duplication of functions and limited view of organisational goals.
Chain of command
Authority
Responsibility and
Span of control
The number of employs which can be effectively and efficiently supervised by a manager. Is it a good thing to have narrow span of control? It depends on the nature of the job and the position one is in the organisation.
Width of span is affected by:
Skills and abilities of the manager
Employee characteristics
Characteristics of the work being done
Similarity of tasks
Complicity of tasks
Physical proximity of subordinates
Standardisation of tasks
Sophistication of the organisations information system
Strength of the organisation’s culture
Preferred style of the manage
More decentralisation
Environment is complex, uncertain.
Lower level managers are capable and experienced at making decisions.
Lower-level managers want to voice and decisions
Decisions are significant.
Corporate culture is open to allowing managers to have a say in what happens.
Companies geographically dispersed.
Formalisation
The degree to which jobs within the organisation or standardise Sanjay extent to which employee behaviour is guided by rules and procedures.
Highly formalised shops of a little discretion over what is to be done. Low formalisation means fewer constraints in how employees to work. Then how to set a boundary between what is like highly formalised and what is low formulas like what is the
| Mechanistic | Organic | |
| Highly specialisation | Cross functional teams | |
| Rajat department lies Asian |
There are no committees and Apple. One person is in charge of Mac, iPhone etc other person is in charge of worldwide marketing and operations.
Teamwork is depending on trusting other folks.
Work on products and work on ideas to make new products.
List down the different structures of your organisation:
Identify the subunits and division
If everybody has worked in a different industry they can be three different organisational structures. The basic output of this activity will be. If they could be a modification in the organisation structure what it would be.
In a restaurant, the work centre is the kitchen. Inside the kitchen, there are several works centres. The work centre has available capacity depending upon the size the amount can be determined. The Golden Temple is more automated than it was before.