Consumer perspective:
Single brand: Same brand under same store. Nike, FabIndia, Zara, Hamley, Titan,
Multiple brand retailing: Big bazaar, Easy Day, Kirana store, DMart.
FDI rules pertaining to Retail: Zara has partnered with Tata but they can run on their own. Retail people sell the products. IKEA, Nike have come to India due to FDI. FDI doesn’t allow 100% ownership which Walmart doesn’t like that is why Walmart hasn’t opened a store in India.
FDI only allows to set up a market place. Flip kart is a Singapore company. Amazon and flip kart only have permission to set up an online store. They directly can’t see anything themselves but bring buyers and sellers. Exactly as MakeMyTrip, which facilitates where the buyers buy from AirBnb, JetAirways and other hotels. Walmart operates as BestPrice in India. They can only do B2B business and not B2C business. FDI allows 100% in single brand retail, cash and carry or wholesale business. One can have 100% ownership but only for B2B, in single brand retail. In Maharashtra, Telangana, such shops are there.
FDI rules is allowed in e-commerce without inventory models. They allow other brands to keep their products in their space but they don’t own it. PolicyBazaar, JustDial is just a marketplace. It doesn’t sell directly, it just gives information. Amazon is not allowed to sell anything directly in India. Amazon branded products aren’t sold by Amazon but by other players like Appario retail private and Cloudtail.
Prion has 100% subsidy called as CloudTail. Amazon has an important stake in CloudTail with Catamaran.
What’s happening between Future Group and Reliance Retail?
Reliance Retail acquired the debt-ridden Future Retail for as much as ₹25,000 crore. Future Group wants to sell itself. Amazon had a deal with Future Group initially. Amazon is trying its best to prevent Reliance dominance. So it went to the favour of Amazon. So Reliance Retail went to the Supreme Court.
Amazon products are sold by Cloudera.
FDI in single brand.
FDI in b2c, 100% Walmart in Business through their best price.
Metro needs Trade licence. If someone has a company card, upto 4 people can enter.
Multichannel marketing refers to the practice of interacting with customers using a combination of indirect and direct communication channels – websites, retail stores, mail order catalogs, direct mail, email, mobile, etc. Future Group will become the first multi channel retailer in the country with complete digital capabilities.
Without multichannel, there’s no omnichannel. The big difference is that omnichannel commerce connects all channels. This means your customer has a seamless experience across all platforms. They won’t know if they are buying online or offline. It’s consistent, seamless. One buys from the store and the bill comes to the phone. Example: Decathlon (billing through mobile phone), LensKart, food can be Zomato and Swiggy but pricing can be different. Reliance mart, Reliance jewel. TATA bought big basket just recently. It acquired 1mg store. Reliance, TATA is going into the multi- channel game where all the big players are. Amazon bought Whole food where the individual can connect through the internet and once an item is picked the company knows and it’s automatically billed. Amazon is trying to be an offline store.
Departmental Store: Fashion like shoppers.DMart, BigBazaar, Vishal MegaMart. They have multiple sections. In retail department stores into fashion and business is called as. They are also called as hyper markets. Category killer example toy shop is when they specialise in toy market. Reliance fresh has 1-2 store.
.DMart, BigBazaar, Vishal MegaMart. They have multiple sections. In retail department stores into fashion and business is called as. They are also called as hyper markets. Category killer example toy shop is when they specialise in toy market. Reliance fresh has 1-2 store.
Supermarkets are the specialty store: Supermarkets deal with groceries. x
If primary they have in food it is called as Discount store.
The major Ps of marketing:
Price: Discount store, the price attraction is more than product. Example: Brand Factory, Max, Vishal Mega Mart. Any discount store which is very large is called as HyperMarket.
Promotion:
Place: Convenience Store where you can buy anything from Vegetable, bread, Tabasco, Milk, etc. You are okay to pay extra. Example: near by Kirana store.
Product: The product attraction is more. Example: ShopperShop, Marks and Spencer is on the product side. Titan, Nike, Adidas, FabIndia, HomeCentre
People:
Speciality store: Specialisation stores are supermarkets which deal with perishable goods too. Example: Amazon Fresh, Grofers, Big Basket, EasyDay, Milk Basket, Reliance Fresh.
Consolation: Merger and acquisition. Aditya Birla buying pantaloons, reliance buying future. TATA looking to acquire AirIndia. TATA has acquired 1mg.
Globalisation: IKEA, DMart is worried about competing with BigBazaar.
Global sourcing: Sourcing people from wherever it can.
Partnership strategy: Vendors make the product. When Walmart goes to Sri Lanka and Bangladesh it helps vendors run their store efficiently and then asks for audited reports. McDonalds taught the farmers to grow potatoes according to the required standards. For high value and time-critical products like medical supplies and many tech products, air cargo is a critical link.
Payback is where you get loyalty points. These points can be redeemed to buy something else from any other store. Suppose you buy from ICICI card, some points will be added which can be redeemed to buy from another store. Example: SBI Rewards.
Out of the box relationship: Reliance has the user data from different business. Mutual funds, SIM cards, broad bande, entertainment channels, jewellery can be bought from Reliance. Amazon prime and Amazon.com has no great relationship but the membership gives a lot of benefit. Airtel gives Disney and Hotstar subscription to get more business share.
Discount store can be much bigger than an average big bazaar in India. US has 1/3rd population of India and 3 times bigger than Indian so they have more area. Tier 1, tier 2 there is very less space in a populated area. HyperMarket is synonymously used with discount stores.
Career in Retail
There’s a lot of data crunching and actuarial in insurance. It’s same in retail, where a lot of data crunching needs to be done. Gross is always higher than net.
Gross profit = revenue- COGS
Net profit = Gross – expenses
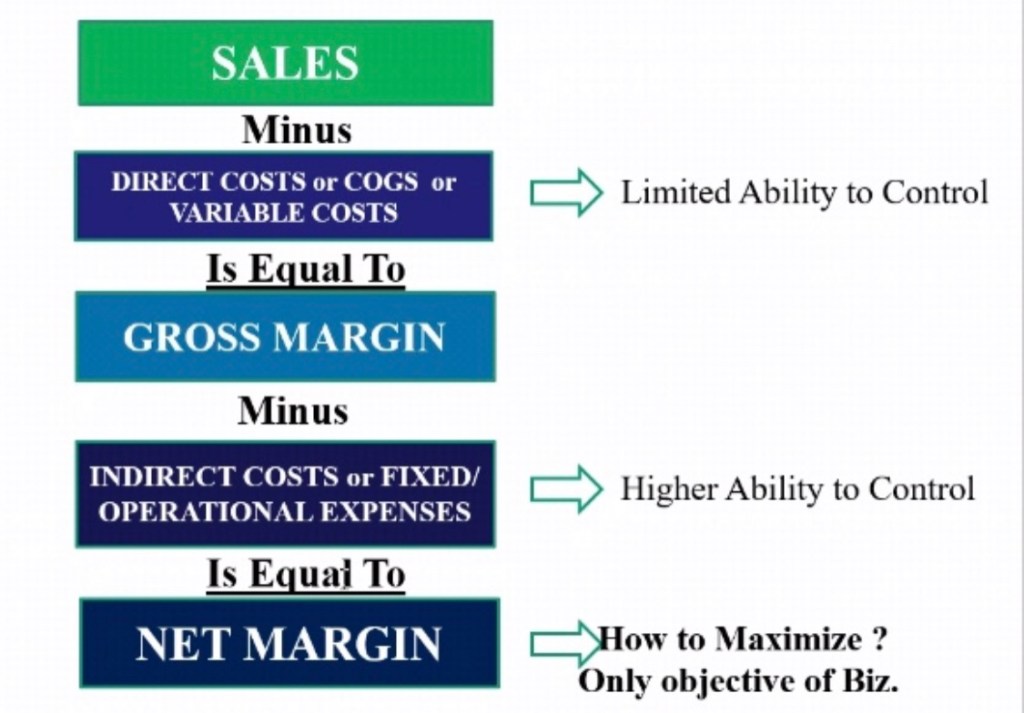
In 100 INR of sales of Walmart they make less than 2 INR. In sale of Tata motors car 15,000 is lost. Titan makes out of 100, INR 4.6 rupees for its shareholders rest goes in other expenses like salary, expenses etc. Automative is going in negative but in its good days it has 5%. Department: Gross margin: 40-60, Net: 6-8%. Tanishq only makes 2k for its shareholders in a 50k necklace. Tata motors has 5-6% net profit in 15,0000 INR. Between gross and net is operating cost like IT, marketing, advertising, tax, etc.
Discount stores like Walmart, DMart etc have 2% -3% net profit margin.
TCS has 15%-20% profitability. Infosys is 13.1% The expenses are the same but since they get their money in dollars that is why they get more profitability. TCS has 5 lakh employees and they are seen in the higher end of salary.
Titan is a 4% game.
ShopperShop: Just 8% goes in the pocket of ShopperShop as marketing and advertisements, Air conditioning, salary. In 4000 INR dress shoppers should makes 4% as a profit is business is going well. In reality, each dress ShopperShop is paying 102 INR for each dress. It is going in a loss.
Suppose they pay 400 INR to the vendor for the 4000 INR dress.
Example: Cost of bread is 30 INR. Kirana person makes 1 inr or 3%.
Operating expenses: It includes rent, electricity, salary. It is given by Gross profit – Net Income.
DMart profitability ratio. Why is DMart more profitable than its competitors like Walmart. DMart is listed in stock market as Avenue supermarket in stock market and it’s known for its operational style which is unique from other players. They do multiple things. They don’t like to be in a posh area. They target small areas and villages. It hasn’t diversified but is in grocery. They have a long term strategy for 25-30 years hence they have purchased the property. They are very clear about their investment.
The mall doesn’t bring the crowd. The DMart brings the crowd. The brand value of DMart is so much that most of the malls want it in their area.
All profits and expenses in a P&L is expressed as a % of sales.
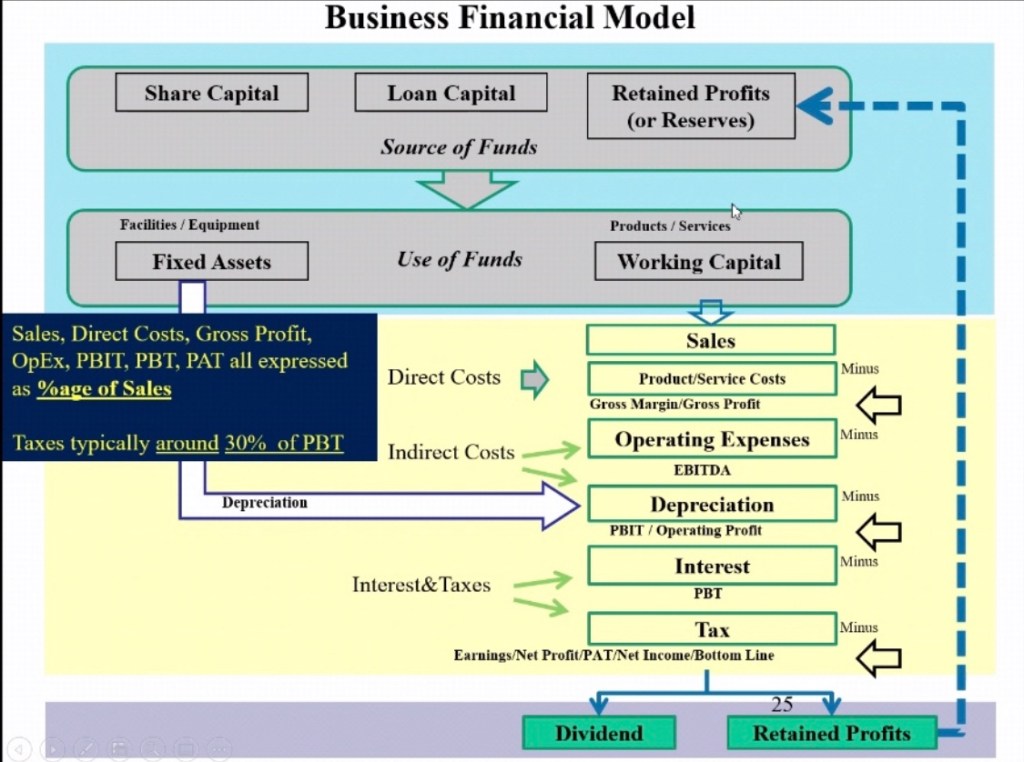
The yellow part is profit and loss.
Direct cost is cost of goods or product bought from someone. Rakesh Jhunjhunwala, believes unless the margin is made the shareholders don’t make a profit. China is very successful as it is able to reduce the price of cost sold. That’s why IT department in India is doing well.
If the organisation is not doing well. Interest and taxation can be negotiated which KingFisher is doing.
Bad debt is when the borrower defaults on paying back. What does it mean in retail environment or manufacturing world? In profit and loss it is taken as expenses. It’s 2-3% in banks. Damage goods or perishable goods
Increase sales or selling in volumes, decrease cost of goods sold by negotiating with the vendors, increase the price (BMW, Apple), decrease expenses like advertisements.
Firing some of the bad-performers in the company.
Renting store needs less money and owning the store needs a lump sum money. Owning store needs huge capital it needs to have 25-30 years future plan.
Profit and loss just has the depreciation cost but not the installation cost of the solar panels. This hugely reduces the operation cost of electricity. For IT, the IT Infrastructure.
With an increase of 1.6% in volume 25000 inr profit is made.
0.5% price increase leads to a profit of 25000 INR.
0.7% decrease in Cost of Goods sold leads to a profit of 25000.
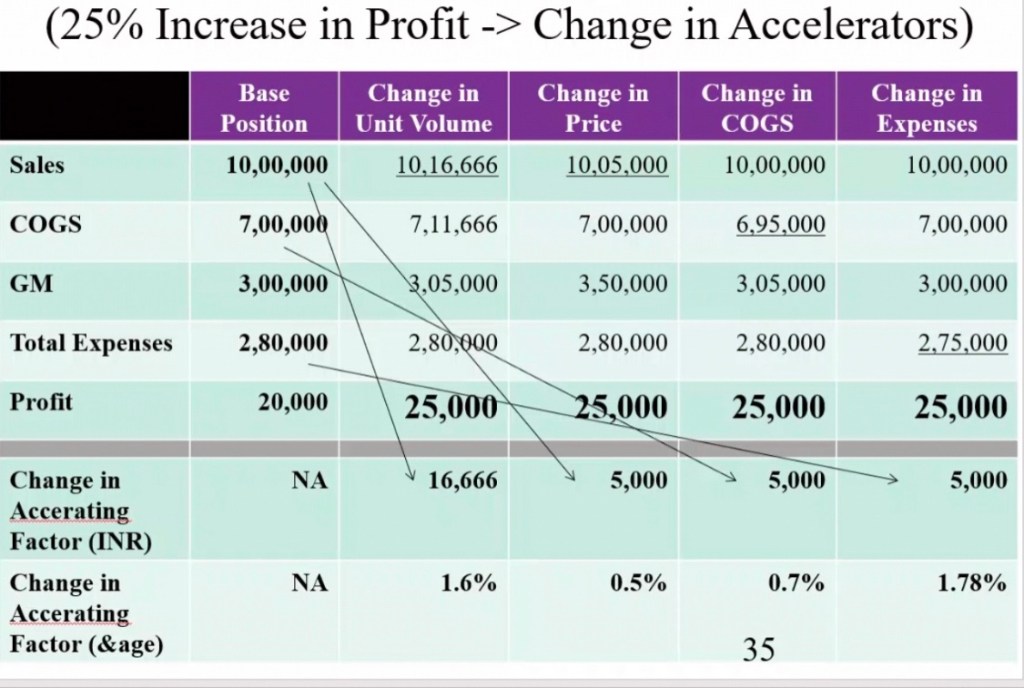
1.78% decrease in expenses like marketing and advertisements, electricity, transportation etc. leads to a profit of 25000.
To attain a net profit of 25% (20000 to 25000) increase the volume by 1.6%
According to the minimum wages law, is any wage fixed for the retail store workers/helpers?
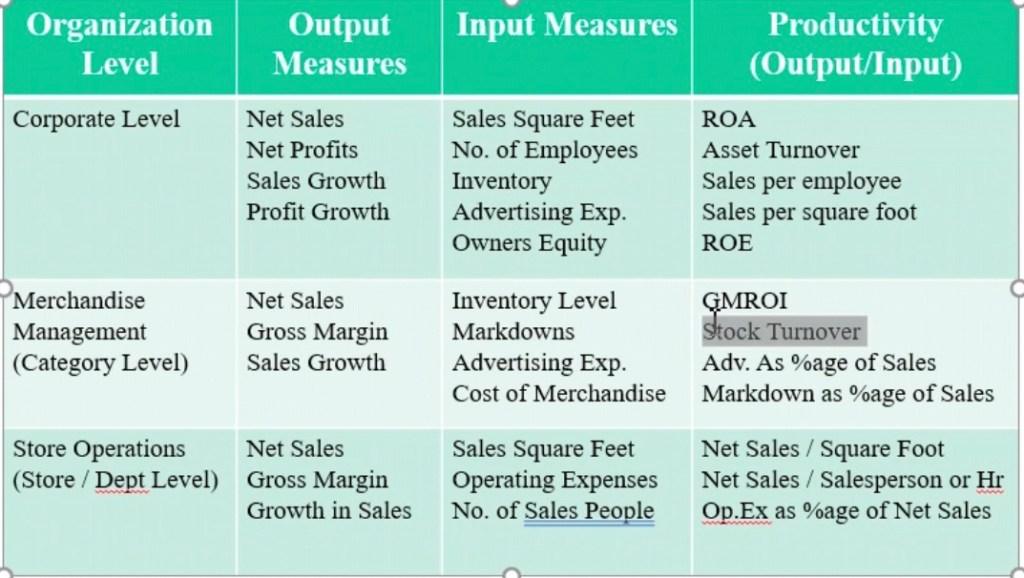
Gross Margin Return on Inventory(GMROI) = Gross Margin/Average inventory cost.
Gross Margin Return on Space= Gross Margin/Sales
How space generates revenue.
GMROL= GM/Employee payroll
Gross Margin Return on Labour
It is how many employees to hire.
Image a ShopperShop which has both menswear and womenwear. The menswear cost of inventory = 5 lakhs. The womenswear cost of inventory = 6L INR. mens wear space = 300 sqft, womenswear space = 400 sqft, menswear = 3 sales people, womenswear = 4 sales people, menswear sales = 7L, womeswear sales = 8L.
Menwear = sales – cogs = GM= 2L
Women wear Gross Margin = 8 – 6 = 2L
GMROL = 2L/3= 66,666
GMROL = 2L/3= 66,666
per employee is giving me 66.66K GM
GMROI for WW = 2/6
GMROF for WW = 2L/400 = 500
GMROL for WW = 2L/4= 50000 inr
Stock turnover ratio: cost of goods sold/average inventory.
It is calculated for a period of 1 year.
Inventory turnover measures how many times in a given period a company is able to replace the inventories that it has sold. How many times the inventory was sold. 500 cars sold in a year. The average has been reused 100 times.
A slow turnover implies weak sales and possibly excess inventory, while a faster ratio implies either strong sales or insufficient inventory.
High volume, low margin industries—such as retailers and supermarkets—tend to have the highest inventory turnover.
Suppose bread is purchased over a period of 2 days. The inventory ratio is 365/2= 182.5 days.
Net sales/average inventory
Supermarket(Reliance Fresh)>Discount(DMart)>Department (Shoppers Shop)>Luxury Retail(Tanishq)
Reliance fresh has vegetable and perishable hence it sells off faster.
Super market: 12-18, DMart: 6-8, Department: Luxury: 2-3, Titan has
What’s the stock turnover ratio for electronic and telecom stores like microwave, fridge, phones.
A permanent price decrease for a product that is at the end of its lifecycle (or “seasonality”).
Imagine you are going to open a retain store(speciality, retail, department store), assuming finance is not an issue, what kind of business would you open?
Electric Vehicle.
DMart store for. Low pricing strategy. It doesn’t pay its employees much but it offers the customers at a lower rate. walmart
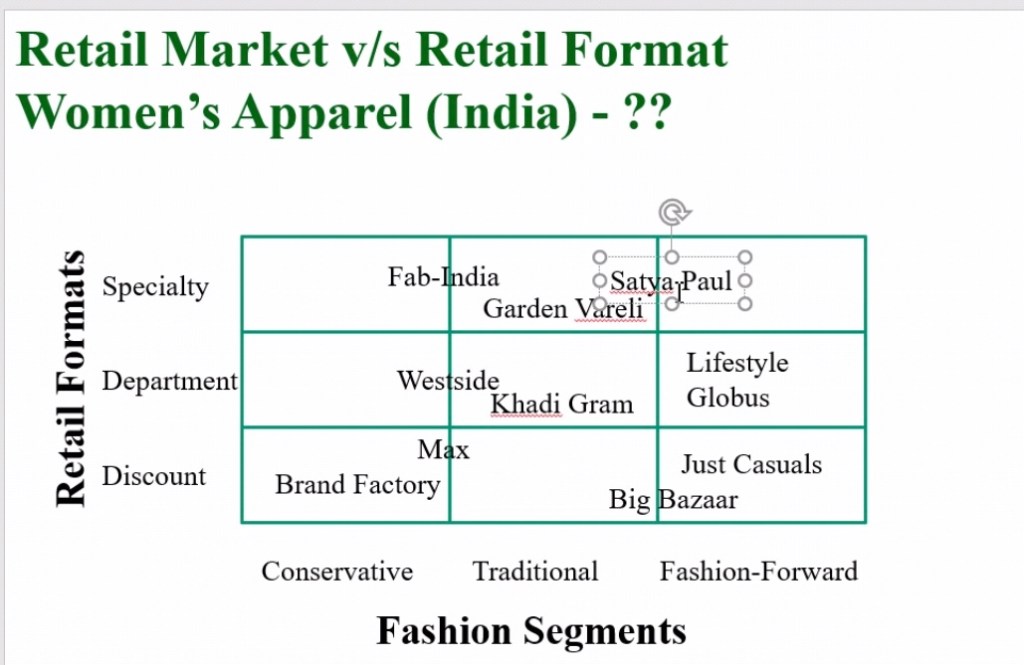
Market strategy
Products, sustainable pricing advantage. Some players differentiating themselves from the market. High price is Baskin and Robbins, low price is natural ice cream and the medium price is Vadilal. Nulli silk is popular in the South, DMart is universal in its appeal, they are focused on geographical western areas rather than spreading themselves thin. DMart is very focused.
Overview of retail processes
RAI: Retail Association of India
Strategic processes(plan): market assessment, strategic positioning, financial planning, procurement, site location and store planning. Sophisticated retailers do it at a weekly level.
NRF: National Retail Federation, Starts with Feb, March, April, May, June, July. Strong customer relation, strong operations. Sunday- Saturday calendar. (5-11)th May is the 14th calendar week or 1st week of may. NRF collects the sales data. Every Thursday have to release the sales date of previous month(green shaded).
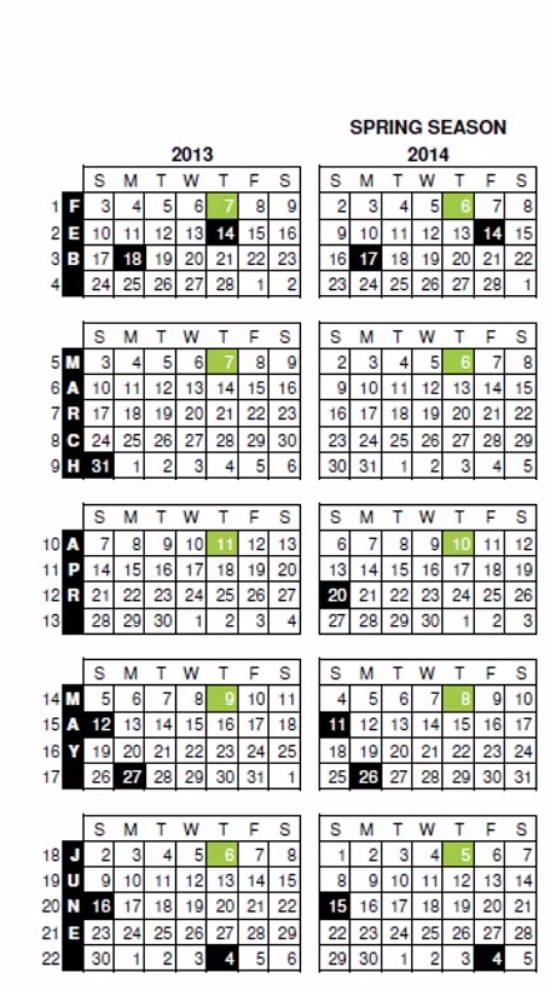
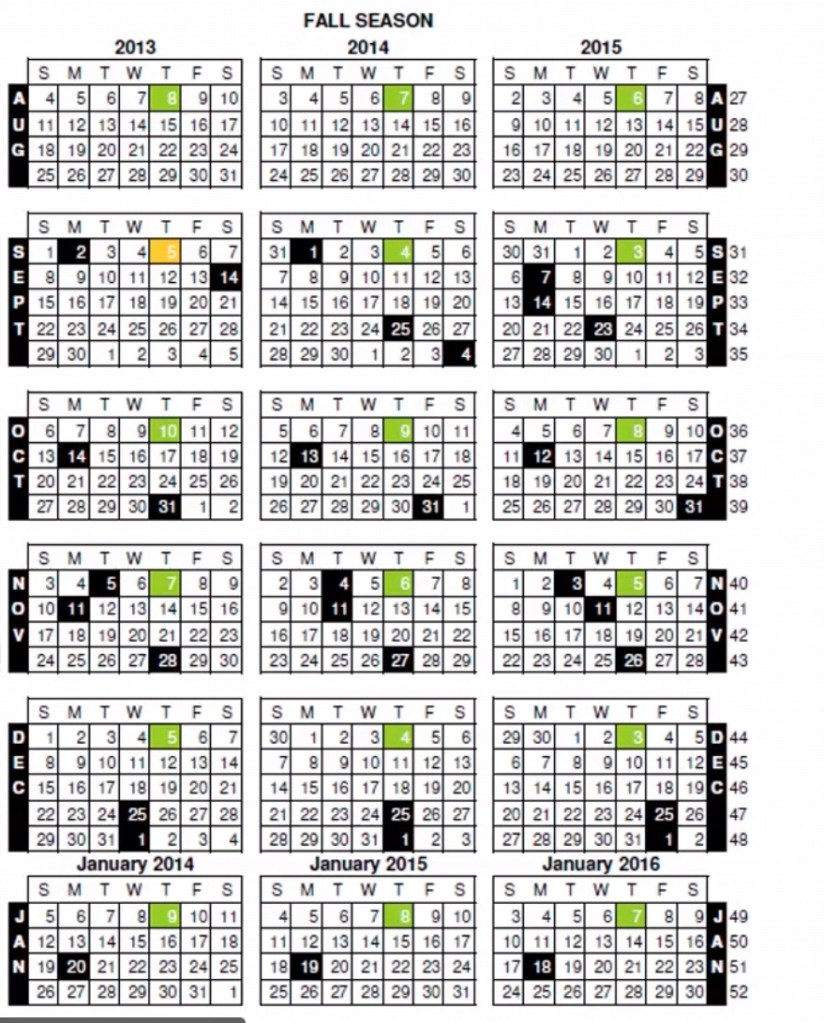
Black shade and yellow shaded. The black box is for the holiday season and the yellow is for the overlap of green and black, means the holiday and the sales reporting falls on the same day.
SIAM: Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturer. In US more than 80% sales is tracked and received.
What frequency the employee appraisal is done in IT company?
Performance assessment could be quarterly (every 3 months) or monthly, especially in IT companies it can be once a year or more than a year. The formal appraisal is done at a yearly level. Spring season the leaves start changing their colours. Fall is after the summer and before the winters. In retail, the business is tracked on a weekly basis. DMart, Zara, Westside have a weekly calendar.
The operational processes:
PLA, buy, move, sell, analyse
Support management involves financial management
SKU: Stock Keeping Unit. Last definition of a product.
SKU stands for “stock keeping unit” and — as the name suggests — it is a number (usually eight alphanumeric digits) that retailers assign to products to keep track of stock levels internally. If a product has different colors and sizes, each variation has a unique SKU number.
A UPC, or universal product code, is a 12-digit numeric code that is attached to products wherever they are sold, for external use. (It’s often referred to as a “UPC code,” awkwardly translating to “universal product code code.”)
Product assortment, also known as product or merchandise mix, is the variety of merchandise that a business offers to customers. Colour, size,
Assortment level for insurance is General and Life. How much health insurance, vehicle, travel insurance. In vehicle there is private.
Financial level planning.
DMart has 300 stores. In the business of retail, the planning is done at the store level. Every store is a profit centre by itself. Region could be Maharashtra, Rajasthan etc. First is corporate level planning, state level planning and within it city level planning. All retailers do their planning at a store level.
First level is the local dimension, time dimensions.
Merchandise planning
- Timely dimension
- Location dimension: For retailers it is store wise.
How much Parle G biscuit will be sold on the third week. How many Levi’s jeans will be sold on 23rd week.
The next process is buying part of the retail dimensions:
1. Location::
2. Product/merchandis
3. Time::
All must realize that any pricing decision is incumbent upon the interplay of “Demand” and “Supply”. Intuitively one can deduct that if demand is high and supply is low, the items would be more costly (price is high) and the price will be low if supply is more than demand.
Stock out:
Store owner has nothing to do with merchandise management. DMart is doing good. They are responsible for sales and for procurement. What products must go to which product and at what time, quantity. They decide what units of Parle G will go to a particular store but they don’t decision which brand will go in a
Merchandise management: procurement, How much to buy I
Open to buy is how much to buy. Planned purchase- merchandise on order – merchandise Received = OTB
Indicator of how much stock to carry for a period of time.
Brands versus private labels
Pricing Strategies
1. Pricing under market: For price conscious customers.
2. Pricing above market:
3. Pricing at market:
Psychological pricing: one price selling
Price – quality pricing : some customers might not like to pay below a certain price for a product.
Odd number of pricing: 4.99 instead of 5.0
Multiple unit price: Buy 2, get at a price of 1.
Markdown is the reduction in original selling price. If it is selling at a peak of the season.
Markdown percentage = (Original selling price- current selling price)/ Selling Price
Reason for markdown: special sale events, competition, clearance.
Discount are temporary, whereas markdown is a permanent change.
So for 150, profit 50 inr. CP: 100. (150-100)/100 = 50%
Margin: (SP-CP)/SP = 50/150*100 = 33.3%
Profit percentage is always calculated on the sales of revenue price. Electricity, IT, advertisements is in percentage of sales.
Cost is 100 INR. Profit margin= 66.66%. Sale/retail price?
2/3 = Selling price – cost price/selling price
Cost is 1/3rd of sales price, if 1/3 is 100 then 300.
Cost is 100, 73% is the profit margin.
0.73 = profit margin. Cost of goods sold is 0.27. COGS of sales is in % of sales.
0.27 of the CP is 100. Then 1 unit is: 370.73 Gross margin/profit is the combination of operating expenses.
Cost: 555, GM= 36%. RP= ? 555/0.64
Cost= 100, GM= 50%, Retail price= 100/0.50 = 200
Break even cost: No profit no loss. Fixed cost/gross profit margin.
If cost is 100, gross profit is 50%. Then the break even point is 200.
Sale price of potato is 24 and the cost price is 15. 10000+ 500 + 15000 + 1000 = 26500 (fixed cost).
SP-CP = (24-15) = 9
9/24 = Profit margin/Gross margin
0.375 % is the profit margin.
Break even point = Fixed cost/ (SP – CP)
26500/9 = 2944 is the break even point.
BEQ = Fixed cost/ (unit sale price – unit variable cost)
Gross margin = unit sale price – unit variable cost.
3200 kg of potato sold. What’s the net profit? The profit starts from 2944. So (SP – break even point)/Gross margin.
(3200-2944)/9 = 256*9
Question: Total expenses = 26500. Expected profit= 5000. Gross margin= 9
Break even quantity = (Fixed cost + expected profits)/gross margin
Break even quantity= 3500. So if we have to make a profit of 5000, we need to make 1500.
1000 crore, operation cost = 30%. Mens wera = 30%, womens= 40%, kids = 15%, footwear = 15%.
Sales target is 30% of 1000 crore which is covered by menswear.
Dimensions of planning and their hierarchies
The purchase price of two gross of dress skirts is $4500 to the wholesaler. Handling cost of these items are 6% of purchase price, which is passed to the retailer. The wholesaler also desires a gross margin of 16%. What will be the selling price to the retail?
CP= 6%*4500.
16% gross margin.
CP= 270
Retail price = 4770/0.84 = 5321.42
Or (4500*1.6)/0.84
The equity market a local shop has adopted a new line of posters. The purchase price per 50 poster is 145$ with 10/10 net of 30. The SP per poster has been set at $8.95. Assuming the equity market pays for the poster within 10 days of the invoice date, what is the % markup, based on selling price?
10% discount within 10 days 10/10 net means normal payment period is 30.
PP= 145, SP= 8.95,
130.5/50 = 2.6
SP= 8.95
GM= 8.95-2.6 = 8.95
A buyer purchased goods at $150. Total markup was $50. What is the % of markup on cost? On selling price ?
Selling price = 150+50
On selling price % markup:
(50/200)*100 = 25%
On cost price% markup.
(50/150 ) * 100 = 33.33%
A line of skis has been offered at $125. The markup is 30% of SP. What’s the total markup. Half a gross was purchased at this price from a wholesale distributor in Colorado.
CP= $125, Gross selling price = 125/(100-30)= 125/0.7, Markup= 30% of SP.
178.5-125= 53.5 = Profit
At the end of the summer one retailer found herself overstock with swimsuits. They had cost her $16 per suit for the 23 suits she had left. In order to make room for ski incidentals she decided to sell the suits at 5% mark up on cost. These suits was selling for dollar $24 during the summer, and 8.5% of the selling price was going to cover handling cost. Does the retailer realise any profit on the sale of these last 23 suits?
CP= 23*16 = 368 (for 23)
Markup/SP= 5% on cost = 16.8 (one swimsuit)
SP= $24
Handling cost= 8.5*0.24 = 2.04
No profit
Markup of 30% of cost is equal to what percentage of the selling price?
Let CP be 100. SP= 130. (30/130)
Mark up or 45% of retail is equal into what percentage of the cost of the goods?
RP= 100, Markup = 145. % of the cost of goods = (145-100)/55
Your fifteen year old brother has ordered 25 gross of firecrackers to sell on Fourth of July. They cost 0.10 a dozen. He asked you what should he price them. You tell him to do a 50% markup. SP= 0.15$ but he should sell at 0.20$ a dozen. Explain in simple language the difference between the two prices.
If the cost is $20 and hundred percent markup on cost is used. What is the final price?
40$
You purchase 100 dozen roses for $500. Your mark them up 150% of cost. What is the price for a single rose?
Price of a single rose = 1250/1200 = 1.041
100 dozen is 1200 roses. 1 dozen is 12.
You are an employee of an apparel shop. The standard mark up for Bansal 75% of cost. The cost of the paint is $17.50. As an employee, you can receive your choice of a 20% discount of the retail price or a 40% discount on cost. Which will you choose?
17.50*1.75= markup = 30.625
20% on 30.63 = 6.12
40% on 17.50 = 7
As a retail buyer you notice that China plate cost is $2.25 each. You need a 75% markup on cost to make it worth buying them. You figure out that you can sell 500 at $4.50, 1000 at $4.00 or 2,000 at $3.75. How many should you purchase?
CP= 2.25. MP= 1.75*2.25. = 3.93
If 500,
Cost 500*2.25 = 1125. Sale = 500*4.5 = 2250. GM= 50% = 1125 inr
If 1000, cost price = 1000*2.25= 2250, sale = 1000*4 = 4000, GM% = 43.75% or 1750 inr.
You advertise a $320 computer printer at 20% off. The printer originally cost you dollar 175. What is your final mark up at the tail on the computer if you sell it at this special price?You are advert is a three $20 computer printer at 20% off. The printer originally cost you dollar 175. What is your final mark up at the tail on the computer if you sell it at this special price?
0.80*320 = 256
CP = 175
(256-175)/256 =
150 winter jackets at $120 each. CP= $76.
Overall CP = 13300 (175 jackets)
SP (120 jackets)= 18000, CP (120 jackets) = 11400
Gross margin= 36.7 = (SP-CP)/SP
Remaining jackets (25) = 4180.
13300/(1-0.25) = 17733= Overall sales
Fixed cost= 1400 + 125 + 200 + 1040 + 1300 =
Break even = fixed cost/(SP-CP) = 5.5 profit per T-shirt
4065/5.5= 739 shirt onwards is profit.
Location Analysis
1. Department stores: mall or outskirts. DMart gets majority of the crowd. Infrastructure quality is also not good so they compromise with their location. Mall needs DMart as it brings maximum crowd.
2. Discount stores: Preference is the outskirts. Shoppers mall needs a good mall.
3. Specialty store: Titan or Tanishq. So mostly MG roads and malls.
a. GDP
b. People’s disposable income
c. Employment rate
d. Optimal routes from the warehouse
e. People in village are likely to buy sachets.
DMart : next to the road shop
Tanishq : shopping mall
Shopper shop: shopping mall
Three ERP choices:
1. SAP, Oracle, JDA for shoppers stop, S/4HANA.
B2B: Vendor portal. Udaan, IndiaMart, JustDial,
Advertisement is done by the marketing team, and promotions is done by the operations team. In 2003, Cadbury had worms in it so Amitabh bachan promoted the product to improve the brand image. Promotion is but one get one get one. Advertisements is to make the people aware, billboard ads, Social Media ads.
Franchise is giving permission to someone to open store . Ellora bakery would be expansion whereas Haldiram would be franchise. Patanjali is an example of franchise. Subway is available for individual franchise. Hilton hotel has a franchise. Sometimes the franchisee just puts the investment and the operations is taken by the franchise. VLCC, Lakmé, Gold gym, multifit, Naturals, BaskinRobbins.
ABC inventory analysis is based on the Pareto Principle. The Pareto Principle states that 80% of the sales volume are generated from the top 20% of the items. It means that the top 20% of the items will generate 80% of the revenue for the business. It is also known as the 80/20 rule. It has to do with merchandise management (for retail) otherwise inventory management. Classification of items such as:
A: Best selling. B: medium class. C: low class. D: worst class.
B: medium class. C: low class. D: worst class.
A has to be always there in terms of Supply Chain and since they will be generating maximum amount of revenue they will be at the front of the shelf. Eggs and bread is class A. Eggs, Maggi noodle is class B. They have to be stocked as soon there is restock level. There is a separate supply chain algorithm. A class items cannot be out of stock else it will be a disaster. C class items like pizza sauce, sauce, high priced chocolate. Even if they are out of stock it is not a disaster. Class D is Lindt chocolate. When you give someone an item to sell and you agree to get paid only after the item has been sold, this is an example of a time when you sell the item on consignment. Promoting because of good margin. Don’t pay for your inventory. Central store is a small mall in operations. It doesn’t own the the inventory . It is outsourced. The future group doesn’t own any inventory inside central store. Consignment could be a supply chain based strategy. Like due to COVID times, people would want ready made chapati but it needs availability and good quality. We have to think about the replenishment.
CAC: Customer acquisition cost. It can be tracked on based of data acquired and gathered. CLV: Customer Lifetime Value. CAC<CLV means less amount is spent on acquiring the customer. Don’t give more discount with people who have low customer lifetime value.
RFM: RFM stands for recency, frequency, and monetary value. The idea is to segment customers based on when their last purchase was, how often they’ve purchased in the past, and how much they’ve spent overall. Customer can be identified by their number, adhar number, etc. It is purchase pattern analysis.
Sell through analysis is related to sales which is comparison with the forecast. Track your sales versus your forecasts. Segment your sell-through rate analysis by product to see which products are selling well and which products are selling poorly. If it is selling well, we can increase the price to increase the margins. We can bundle the offer with a slow selling item. It will determine the pricing and the promotional strategies.
What is multi-attribute analysis?